Deposition Date
2013-02-01
Release Date
2013-07-17
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3ZLJ
Keywords:
Title:
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF FULL-LENGTH E.COLI DNA MISMATCH REPAIR PROTEIN MUTS D835R MUTANT IN COMPLEX WITH GT MISMATCHED DNA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12 (Taxon ID: 83333)
SYNTHETIC CONSTRUCT (Taxon ID: 32630)
SYNTHETIC CONSTRUCT (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
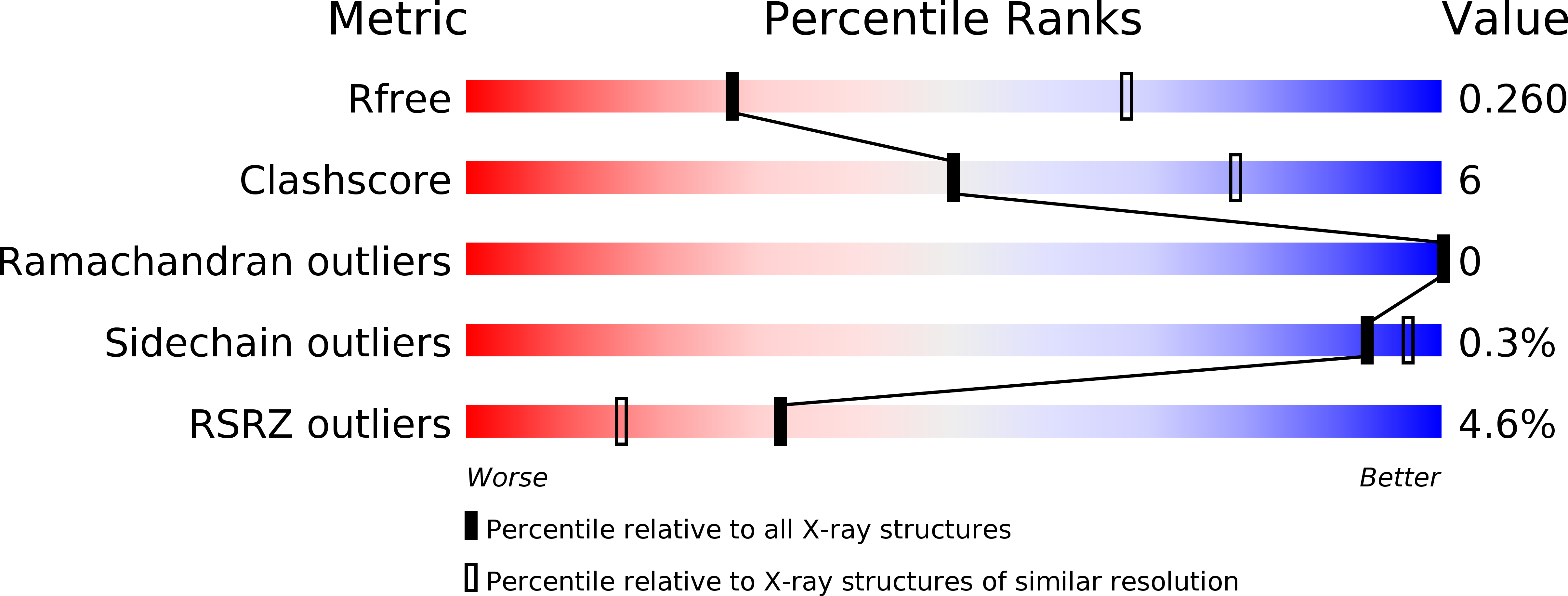
Resolution:
3.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 1 21 1