Deposition Date
2013-07-26
Release Date
2013-10-23
Last Version Date
2023-11-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3WG5
Keywords:
Title:
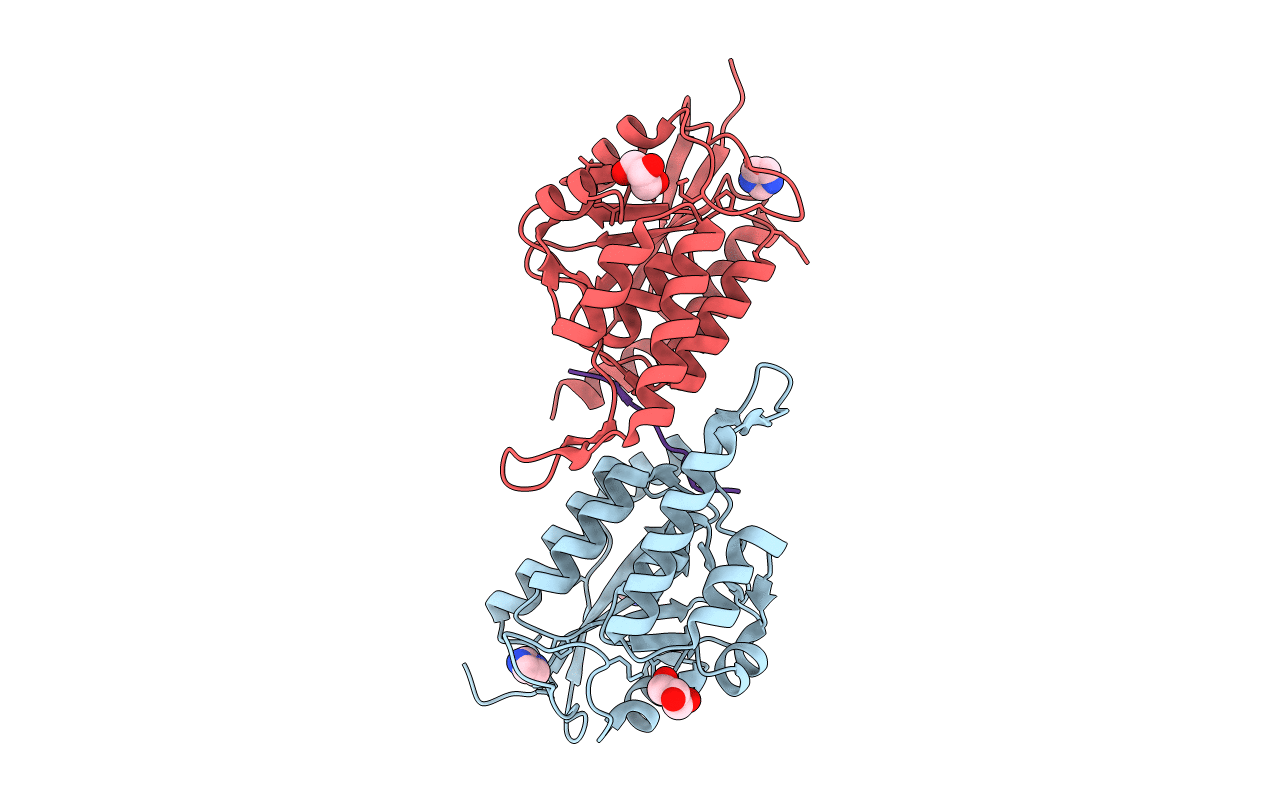
1510-N membrane-bound stomatin-specific protease K138A mutant in complex with a substrate peptide under heat treatment
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pyrococcus horikoshii (Taxon ID: 70601)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
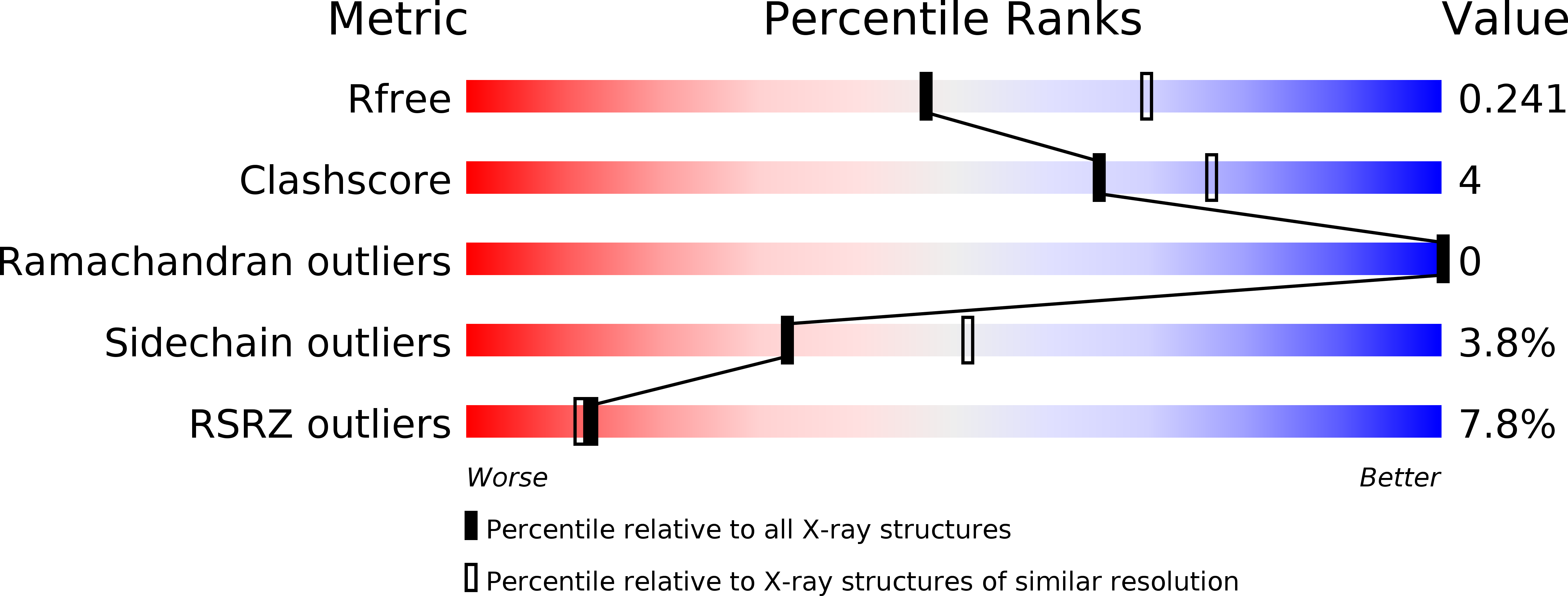
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 43 21 2