Deposition Date
2013-05-29
Release Date
2014-01-22
Last Version Date
2023-12-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3WCO
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the depentamerized mutant of N-terminal truncated selenocysteine synthase SelA
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Aquifex aeolicus (Taxon ID: 224324)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
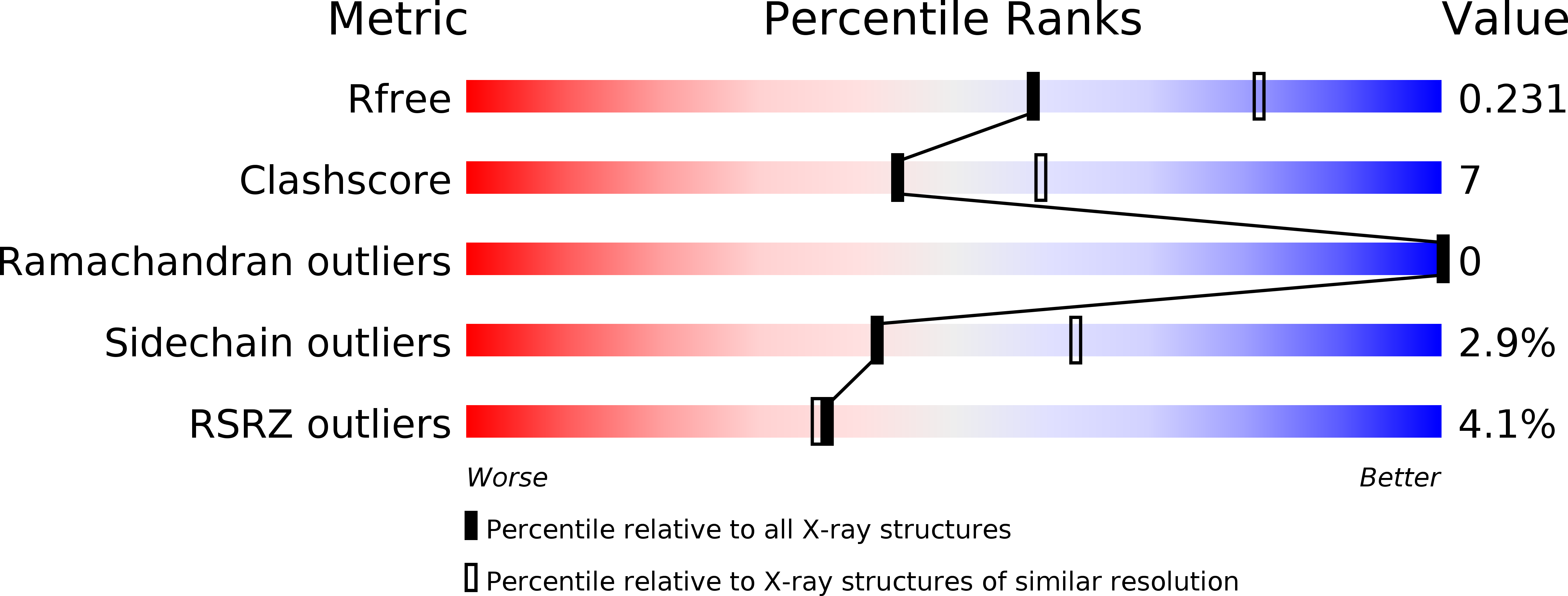
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1 21 1