Deposition Date
2011-10-31
Release Date
2012-04-04
Last Version Date
2023-11-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3UET
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of alpha-1,3/4-fucosidase from Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis D172A/E217A mutant complexed with lacto-N-fucopentaose II
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (Taxon ID: 391904)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
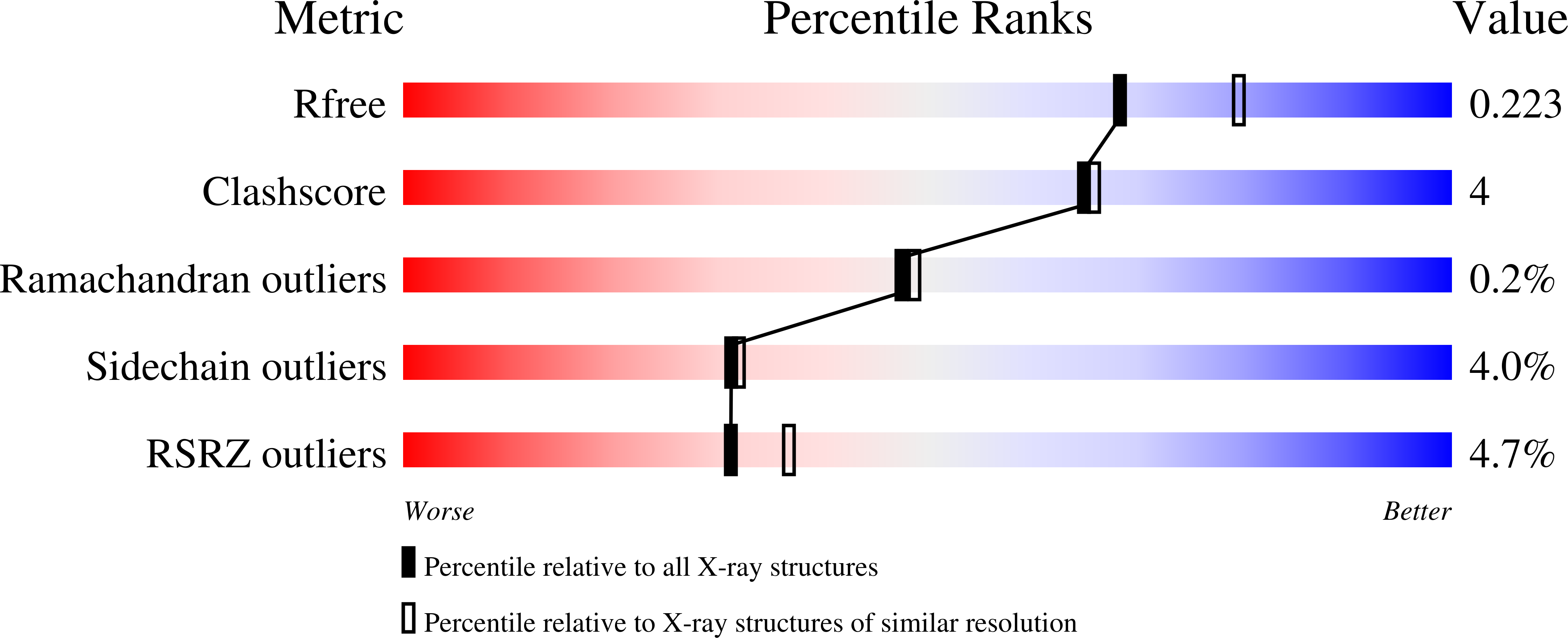
Resolution:
2.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21