Deposition Date
2011-09-26
Release Date
2012-03-14
Last Version Date
2023-09-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3TYL
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of neuronal nitric oxide synthase heme domain in complex with 6-(((3S,4S)-4-(2-((2-fluorobenzyl)amino)ethoxy)pyrrolidin-3-yl)methyl)-4-methylpyridin-2-amine
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rattus norvegicus (Taxon ID: 10116)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
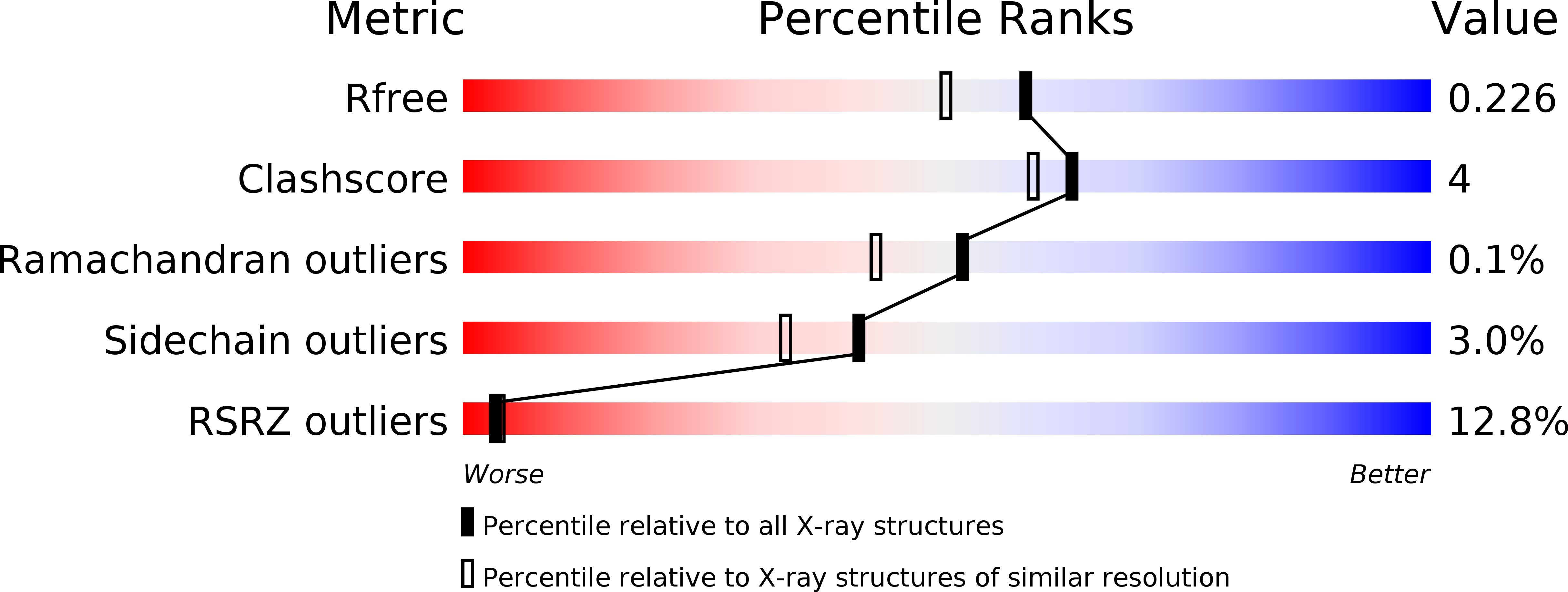
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21