Deposition Date
2011-08-29
Release Date
2012-01-11
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3TL8
Keywords:
Title:
The AvrPtoB-BAK1 complex reveals two structurally similar kinaseinteracting domains in a single type III effector
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Arabidopsis thaliana (Taxon ID: 3702)
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Taxon ID: 323)
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Taxon ID: 323)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
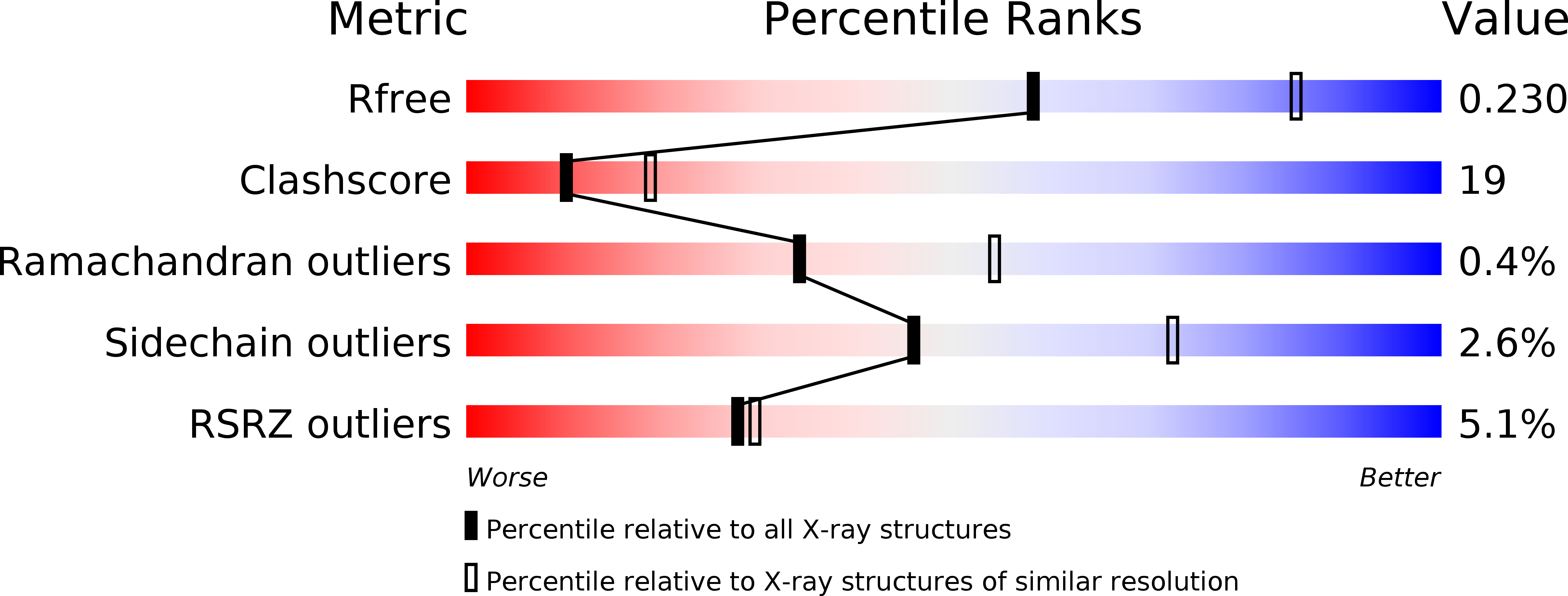
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1 21 1