Deposition Date
2011-03-04
Release Date
2011-11-30
Last Version Date
2024-03-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3QYY
Keywords:
Title:
A Novel Interaction Mode between a Microbial GGDEF Domain and the Bis-(3, 5 )-cyclic di-GMP
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Taxon ID: 340)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
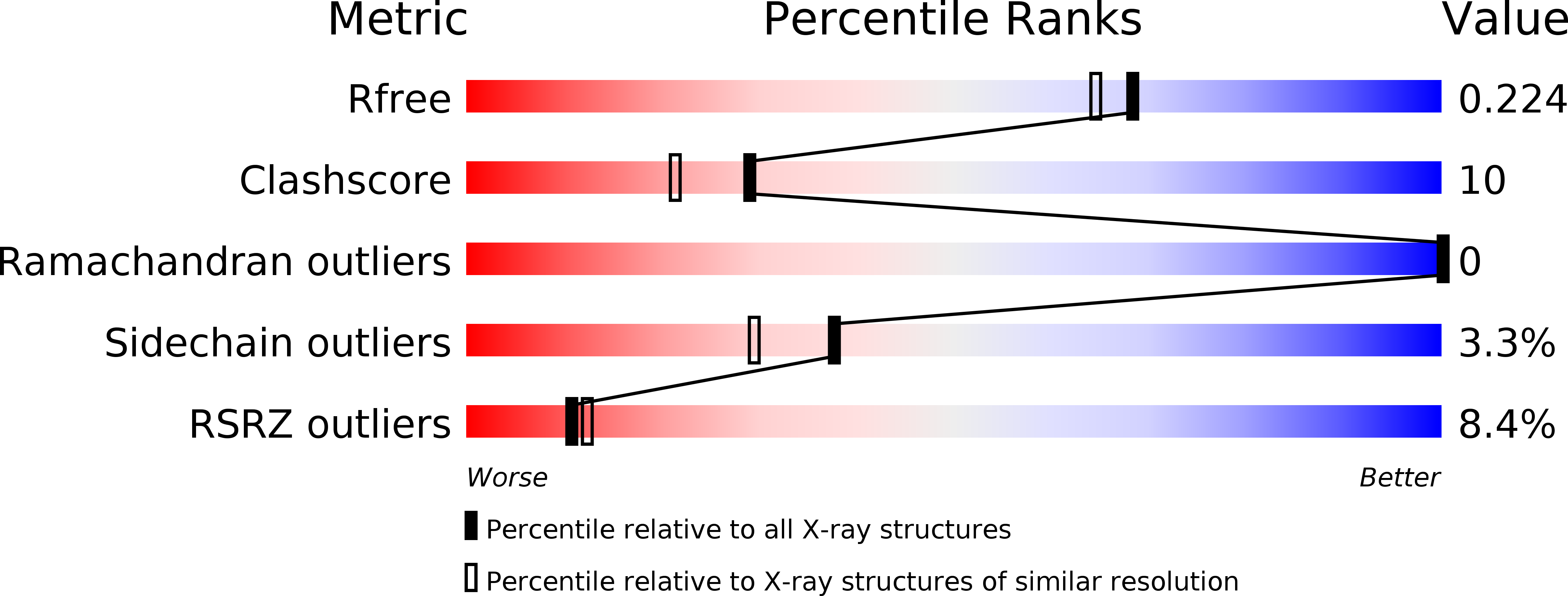
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.20
Space Group:
P 43 21 2