Deposition Date
2010-09-17
Release Date
2011-08-31
Last Version Date
2024-02-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3OW9
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of an amyloid forming peptide KLVFFA from amyloid beta, alternate polymorph II
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.80 Å
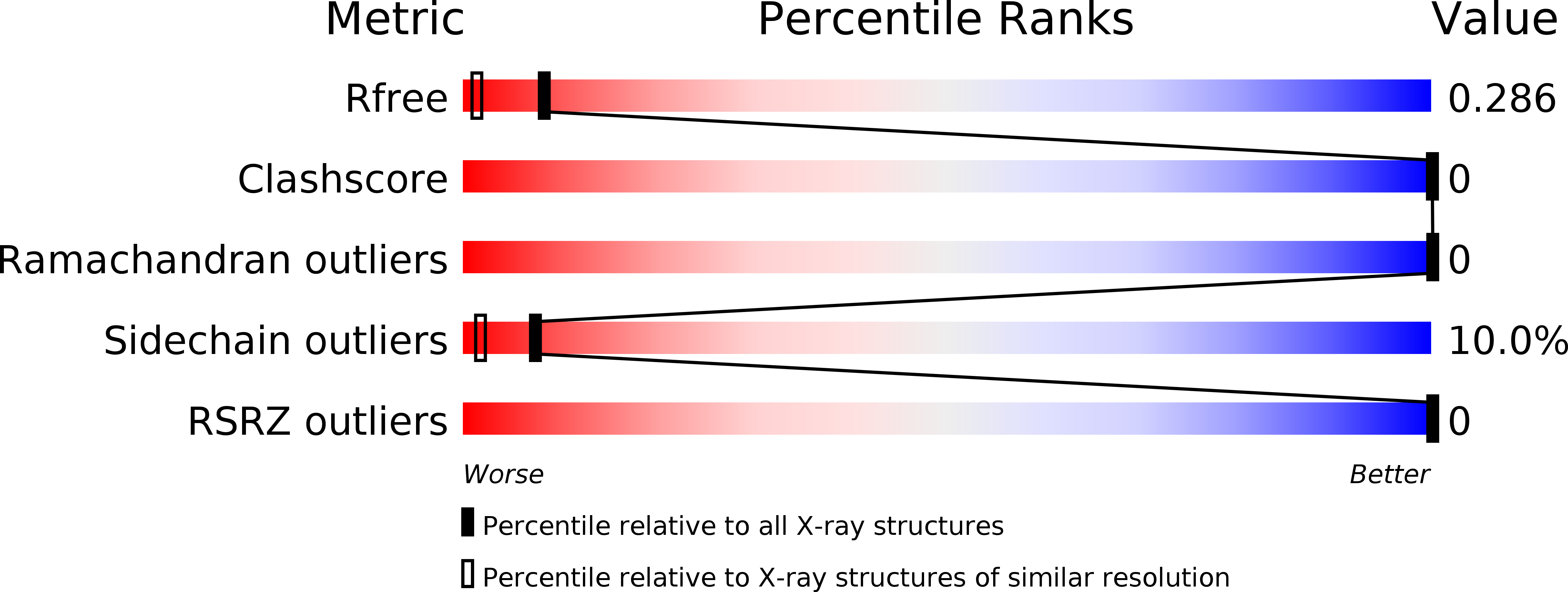
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
C 1 2 1