Deposition Date
2010-06-08
Release Date
2010-07-14
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3NE8
Keywords:
Title:
The crystal structure of a domain from N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase of Bartonella henselae str. Houston-1
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bartonella henselae (Taxon ID: 38323)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
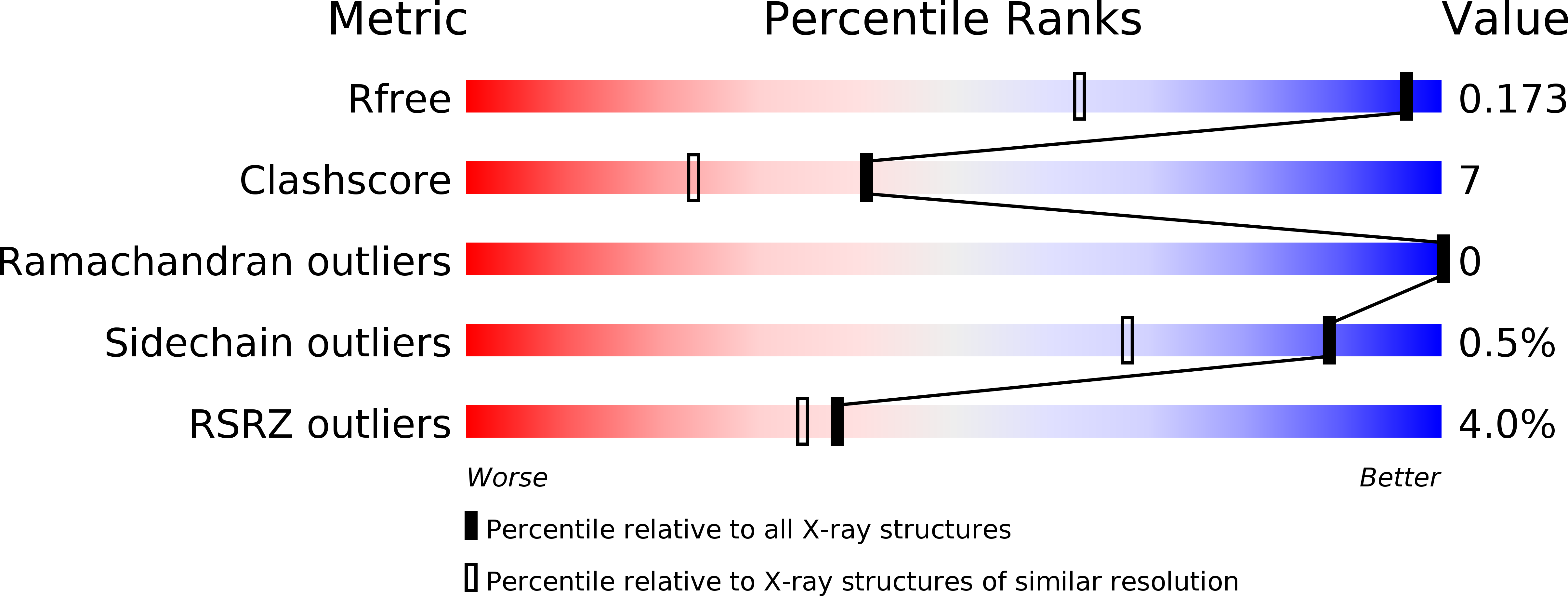
Resolution:
1.24 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
C 1 2 1