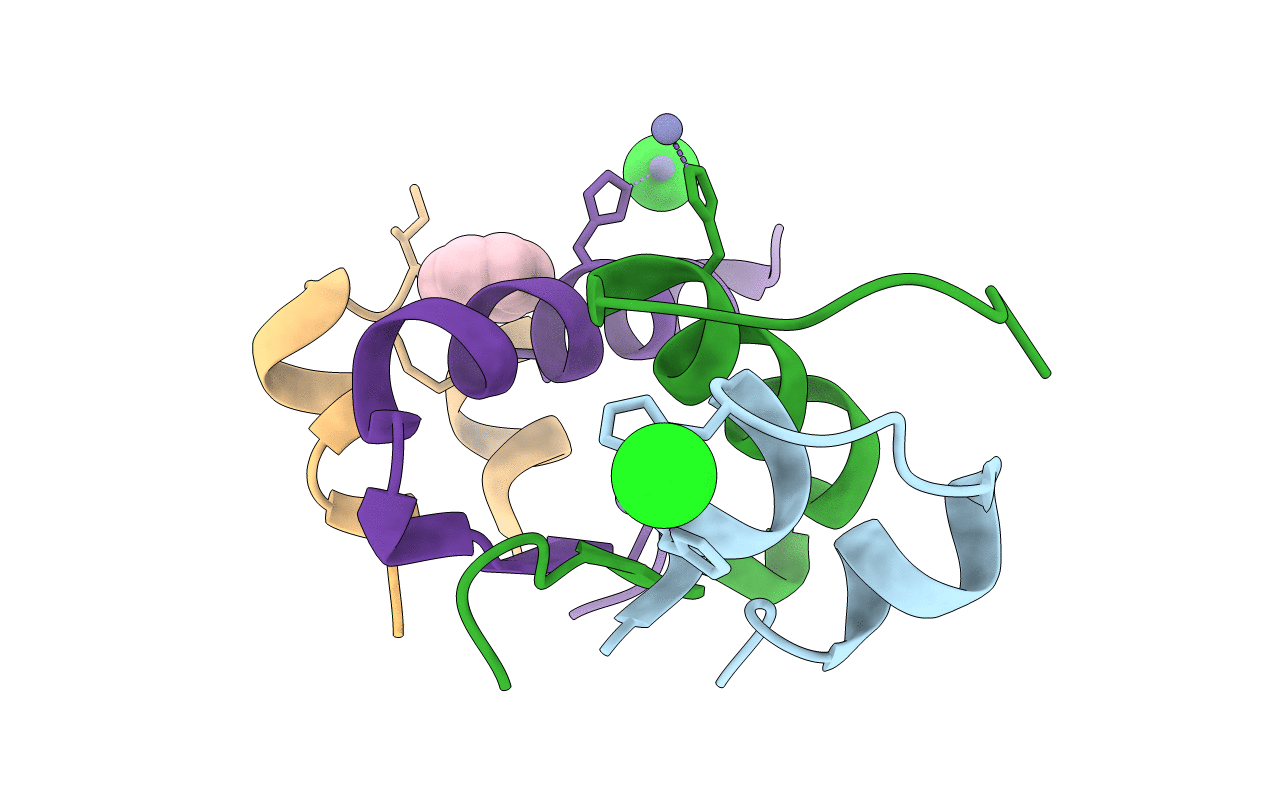
Deposition Date
2009-11-17
Release Date
2010-02-23
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3KQ6
Keywords:
Title:
Enhancing the Therapeutic Properties of a Protein by a Designed Zinc-Binding Site, Structural principles of a novel long-acting insulin analog
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.19
Space Group:
H 3


