Deposition Date
2009-10-14
Release Date
2009-11-10
Last Version Date
2023-11-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3K8E
Keywords:
Title:
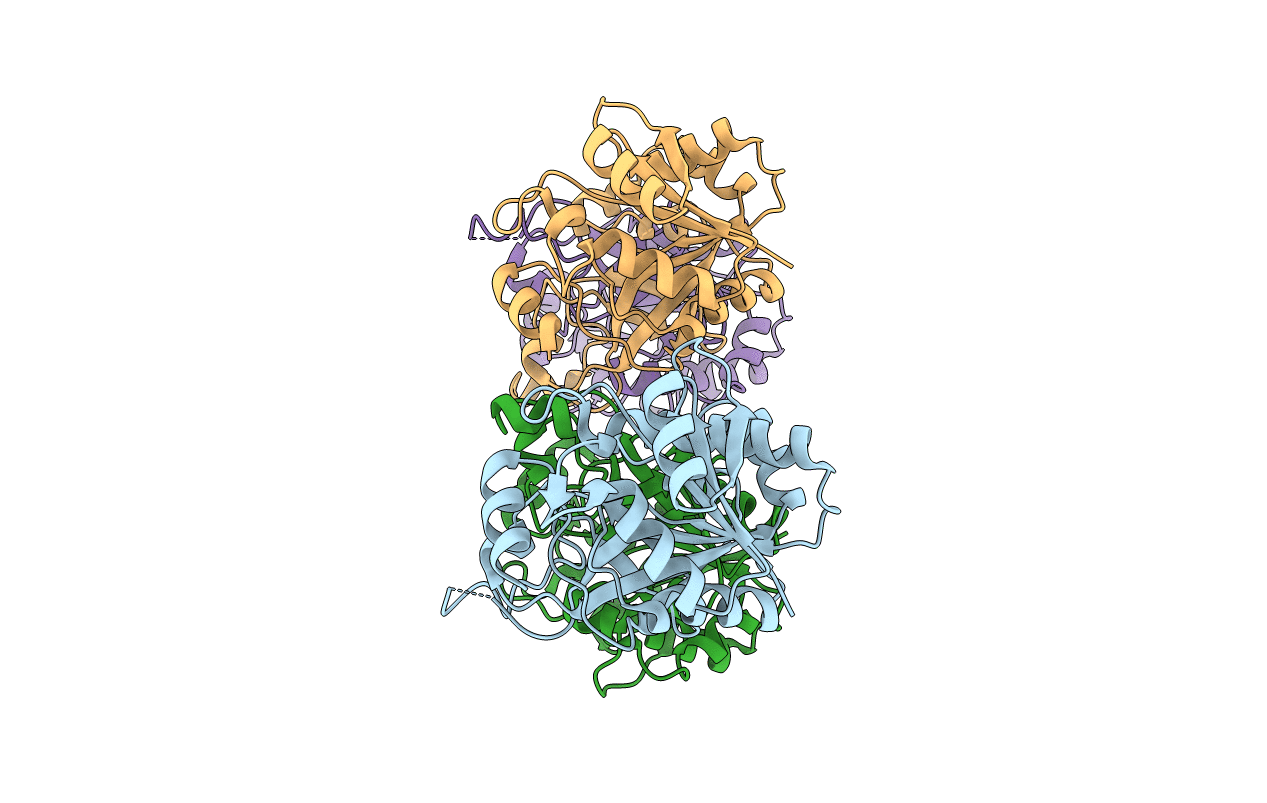
Crystal structure of E. coli lipopolysaccharide specific CMP-KDO synthetase
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 83333)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
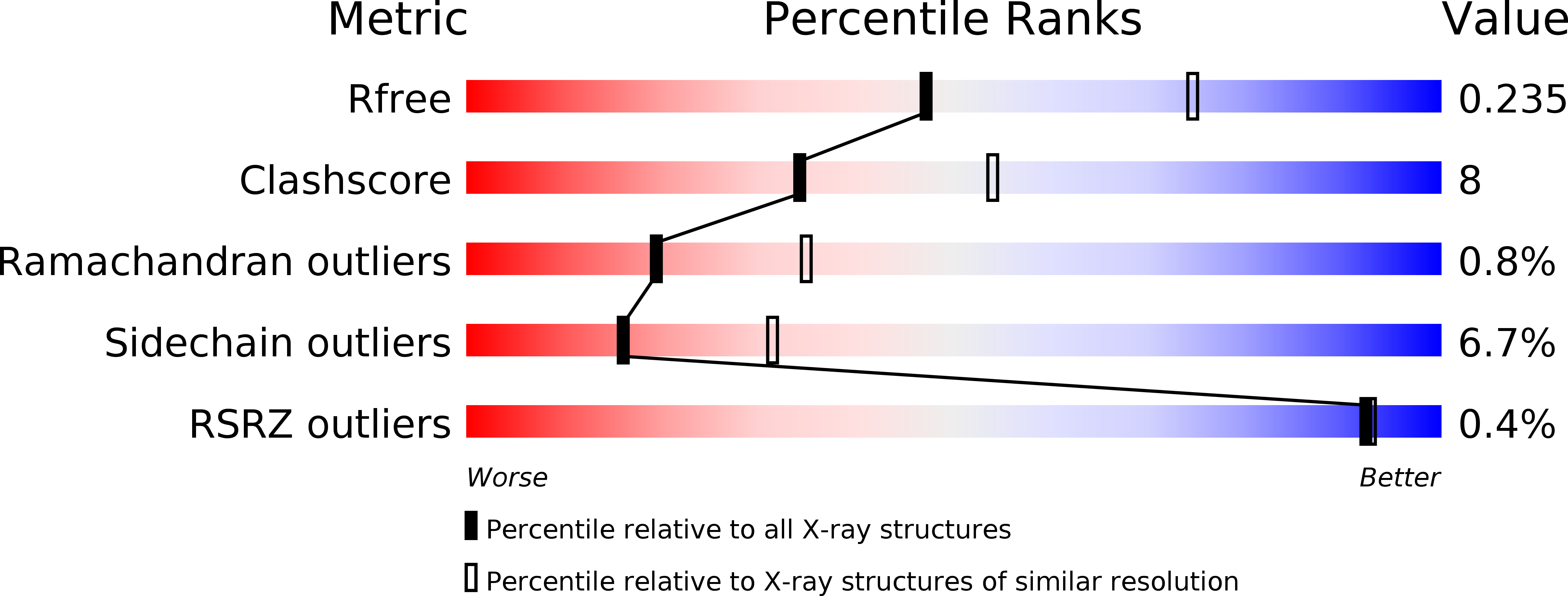
Resolution:
2.51 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 1 2 1