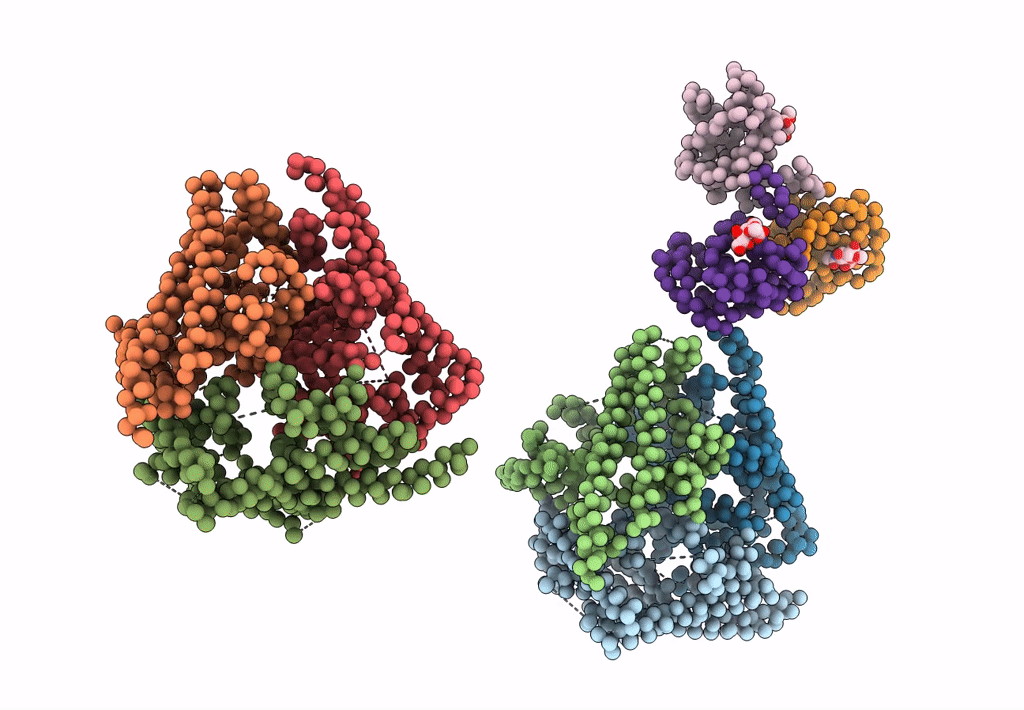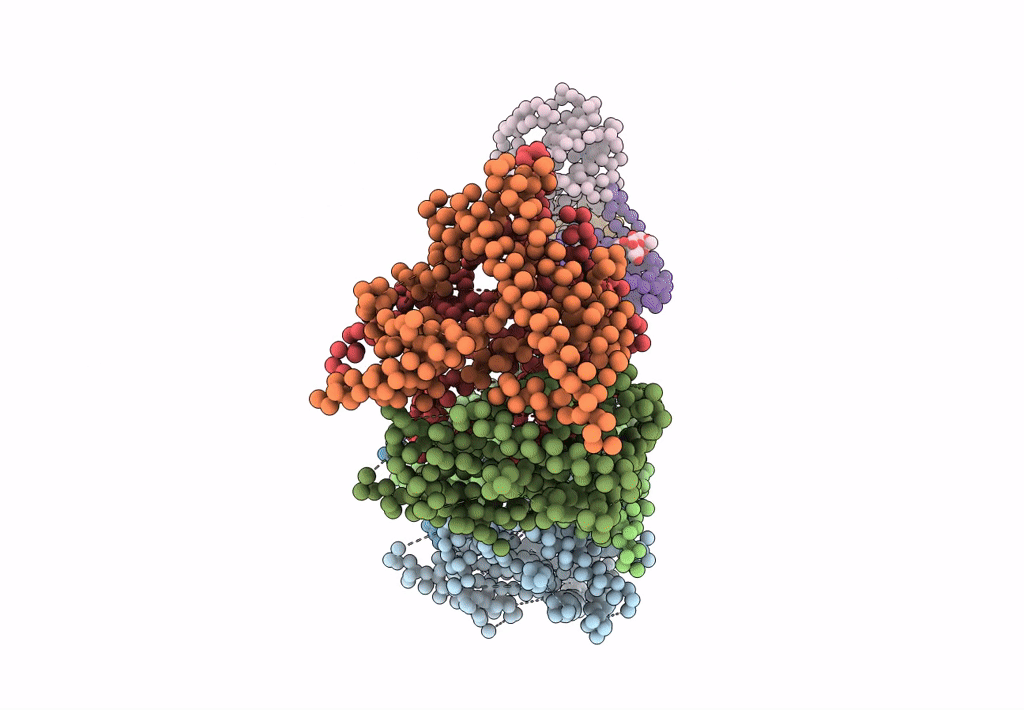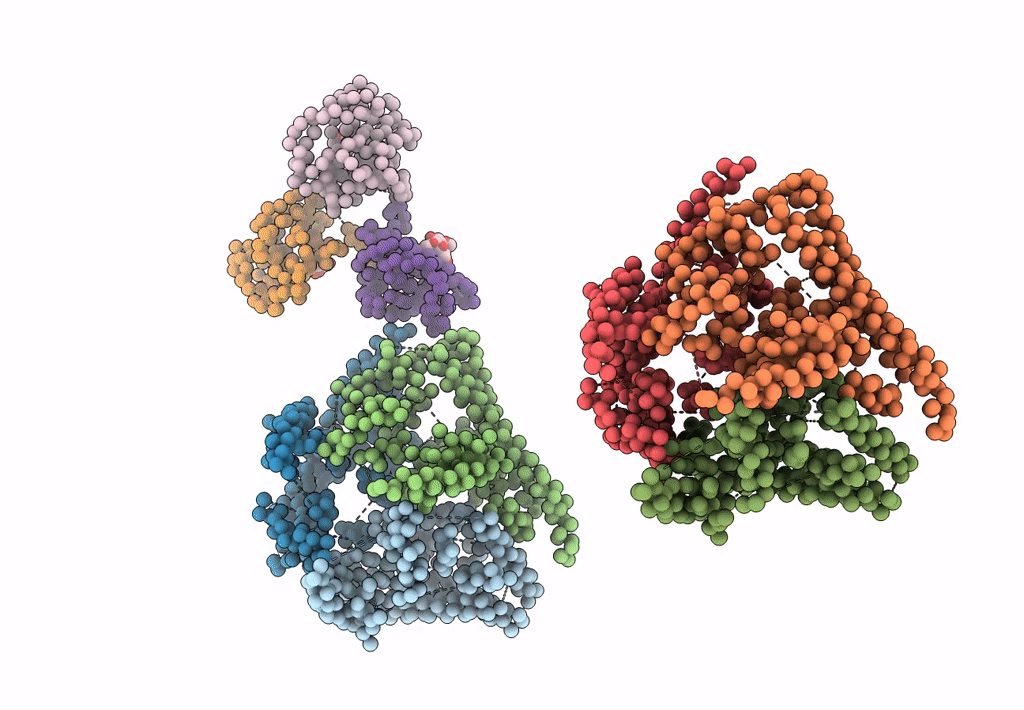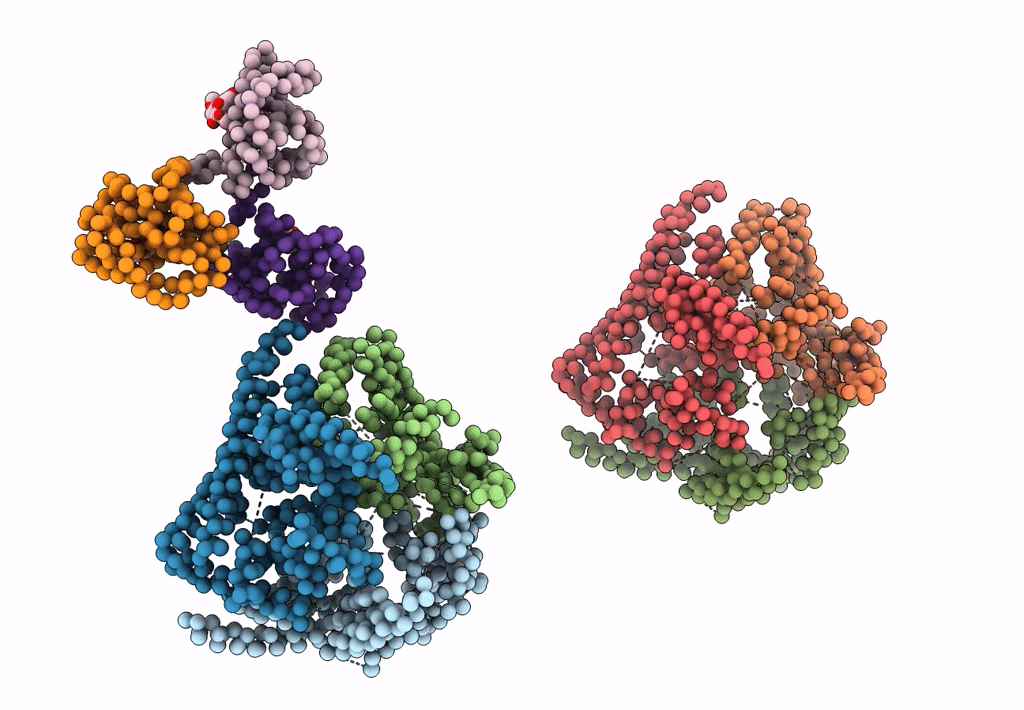
Deposition Date
2010-01-25
Release Date
2010-04-07
Last Version Date
2024-02-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3IYK
Keywords:
Title:
Bluetongue virus structure reveals a sialic acid binding domain, amphipathic helices and a central coiled coil in the outer capsid proteins
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bluetongue virus (Taxon ID: 40051)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
7.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE