Deposition Date
2009-09-03
Release Date
2010-04-21
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3IWY
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of human MDM2 complexed with D-peptide (12 residues)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
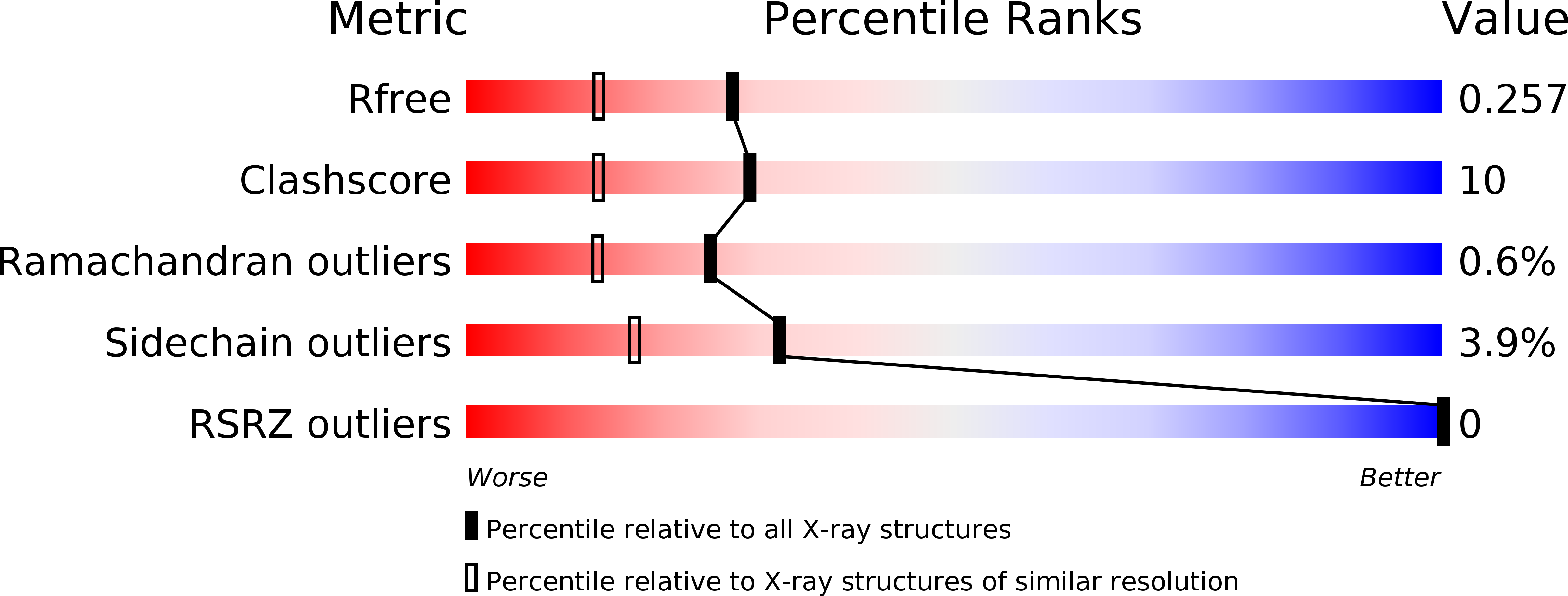
Resolution:
1.93 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 1 21 1