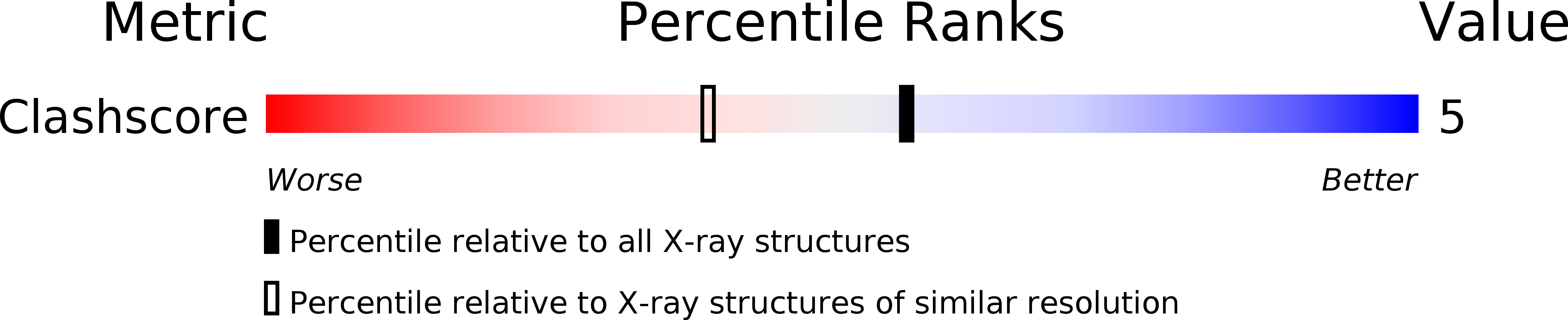
Deposition Date
2008-09-09
Release Date
2008-09-30
Last Version Date
2023-11-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3EFI
Keywords:
Title:
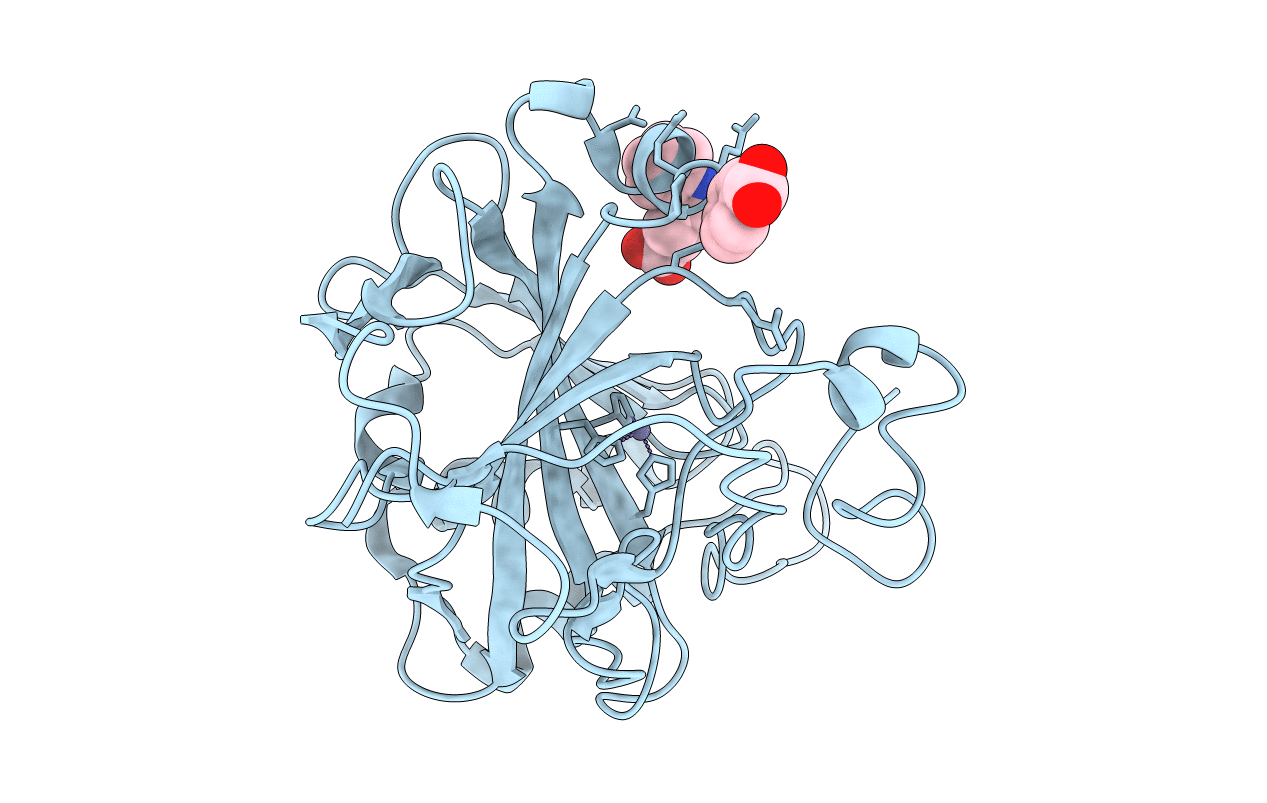
Carbonic anhydrase activators: Kinetic and X-ray crystallographic study for the interaction of d- and l-tryptophan with the mammalian isoforms I-XIV
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.75 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 1 21 1