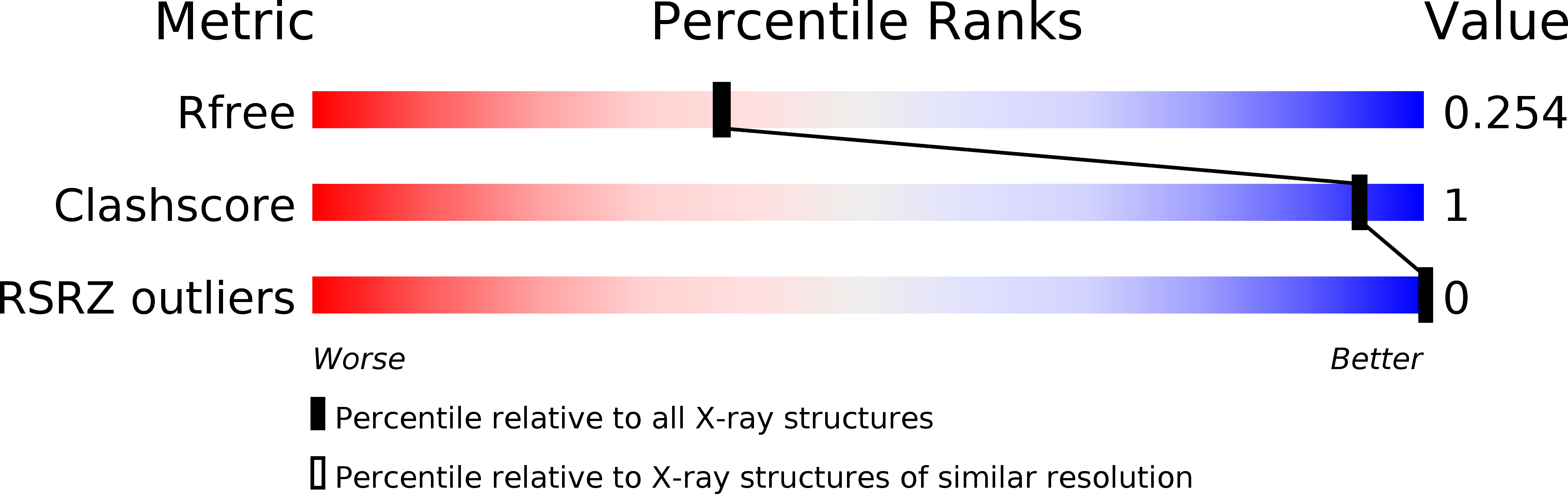Deposition Date
2008-03-27
Release Date
2008-06-10
Last Version Date
2024-02-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3CO3
Keywords:
Title:
X-Ray Crystal Structure of a Monofunctional Platinum-DNA Adduct, cis-{Pt(NH3)2(pyridine)}2+ Bound to Deoxyguanosine in a Dodecamer Duplex
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.16 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
C 2 2 21