Deposition Date
2007-11-26
Release Date
2008-07-29
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3BG4
Keywords:
Title:
The crystal structure of guamerin in complex with chymotrypsin and the development of an elastase-specific inhibitor
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Hirudo nipponia (Taxon ID: 42736)
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
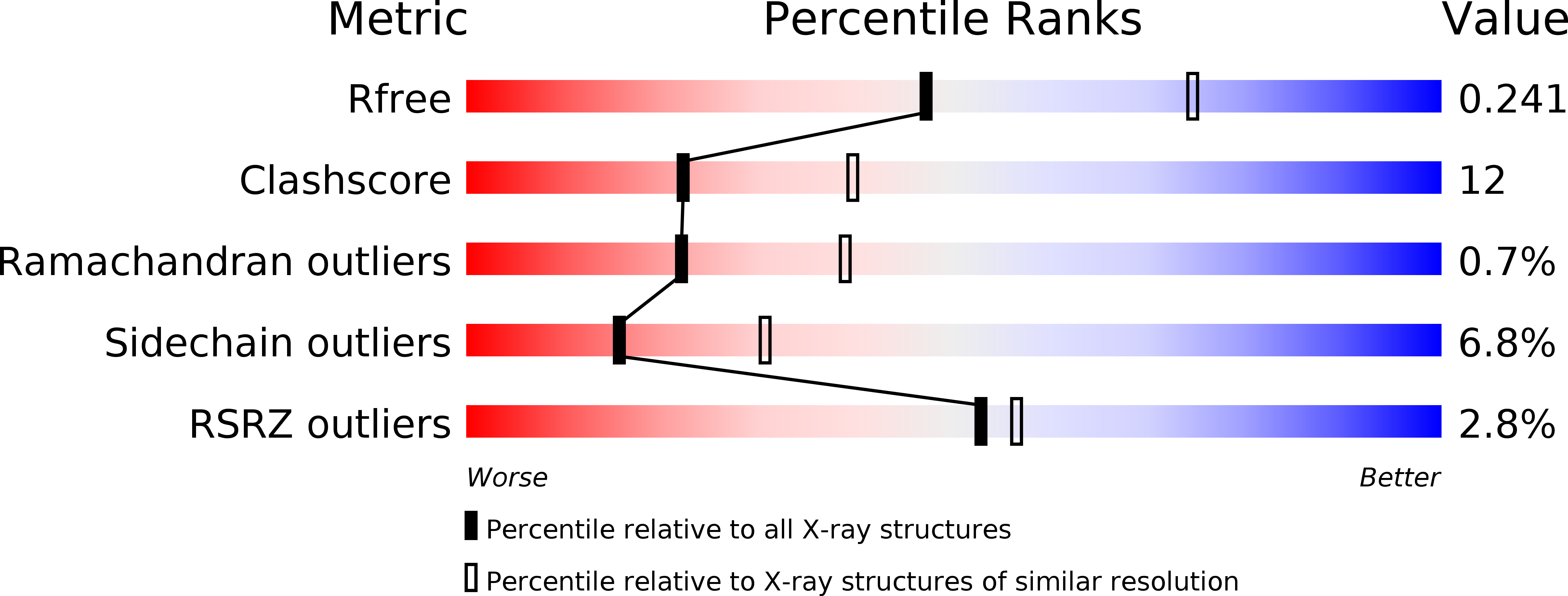
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21