Deposition Date
2011-03-29
Release Date
2012-04-04
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
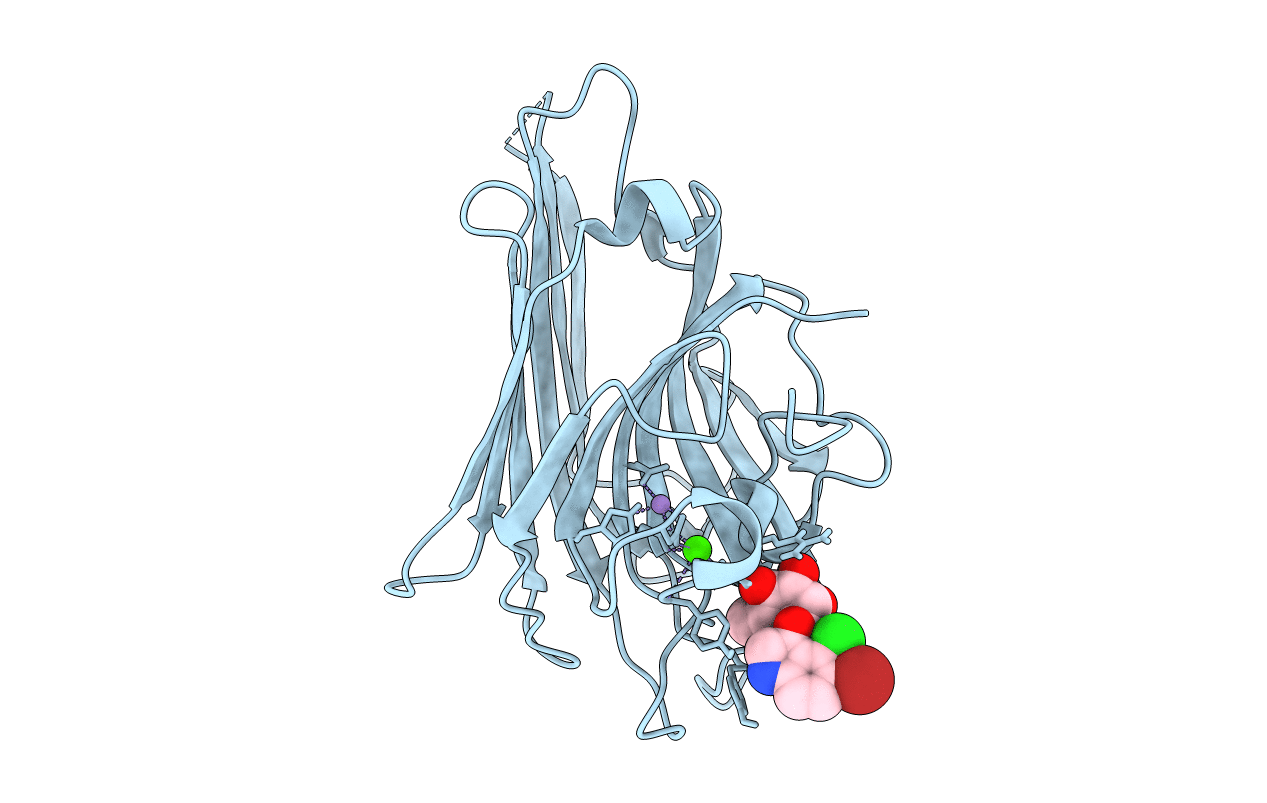
PDB ID:
3AX4
Keywords:
Title:
Three-dimensional structure of lectin from Dioclea violacea and comparative vasorelaxant effects with Dioclea rostrata
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Dioclea violacea (Taxon ID: 192415)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
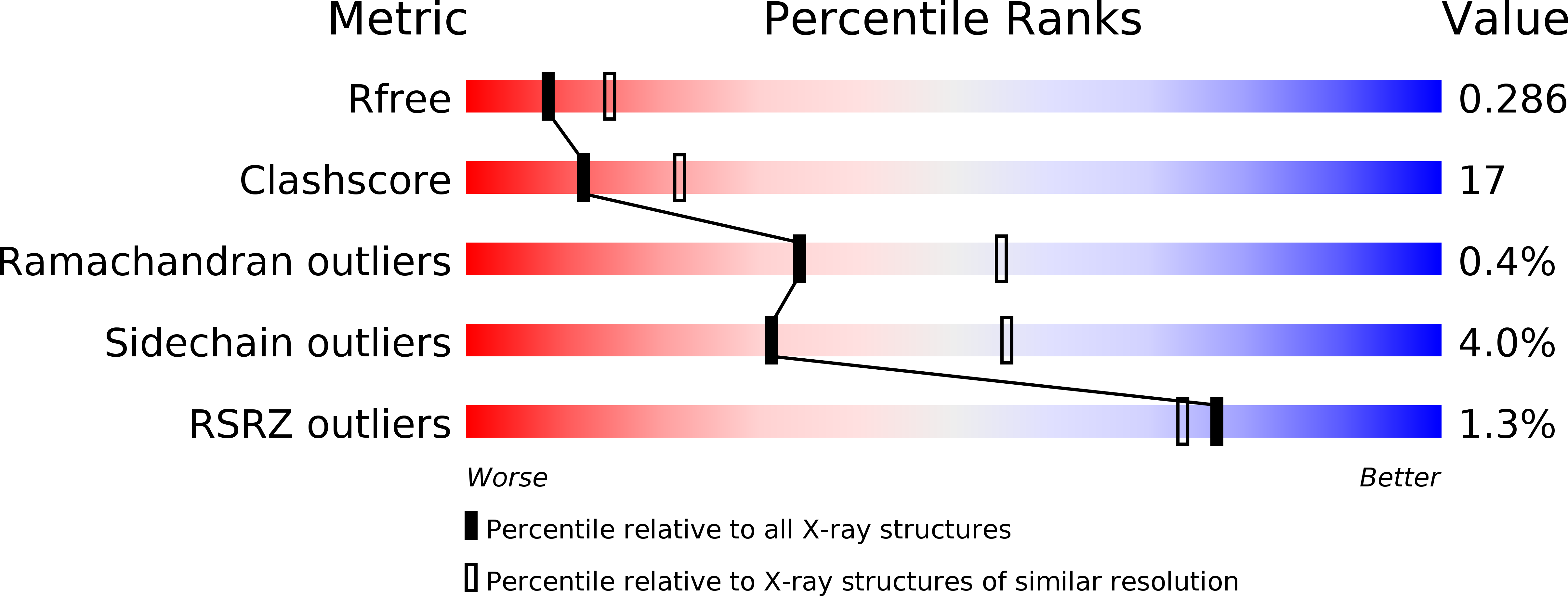
Resolution:
2.61 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
I 2 2 2


