Deposition Date
1987-06-22
Release Date
1988-01-16
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3APR
Keywords:
Title:
BINDING OF A REDUCED PEPTIDE INHIBITOR TO THE ASPARTIC PROTEINASE FROM RHIZOPUS CHINENSIS. IMPLICATIONS FOR A MECHANISM OF ACTION
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhizopus microsporus var. chinensis (Taxon ID: 4843)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
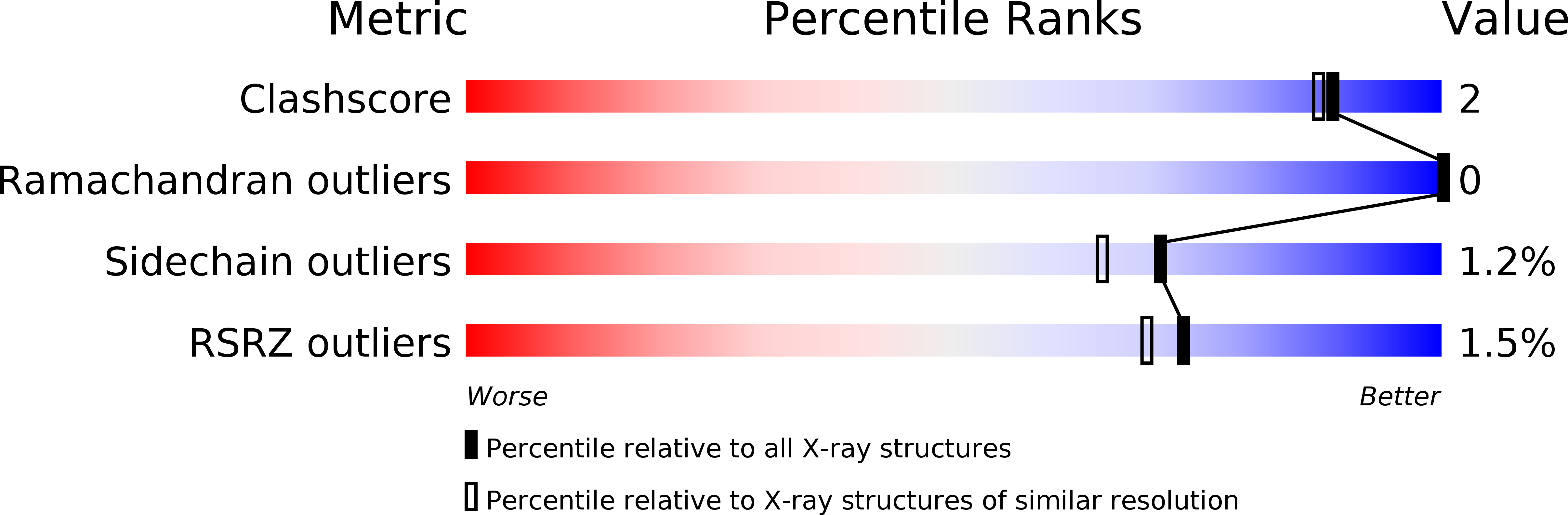
Resolution:
1.80 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 21 21 21