Deposition Date
2009-08-26
Release Date
2009-12-15
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3A69
Keywords:
Title:
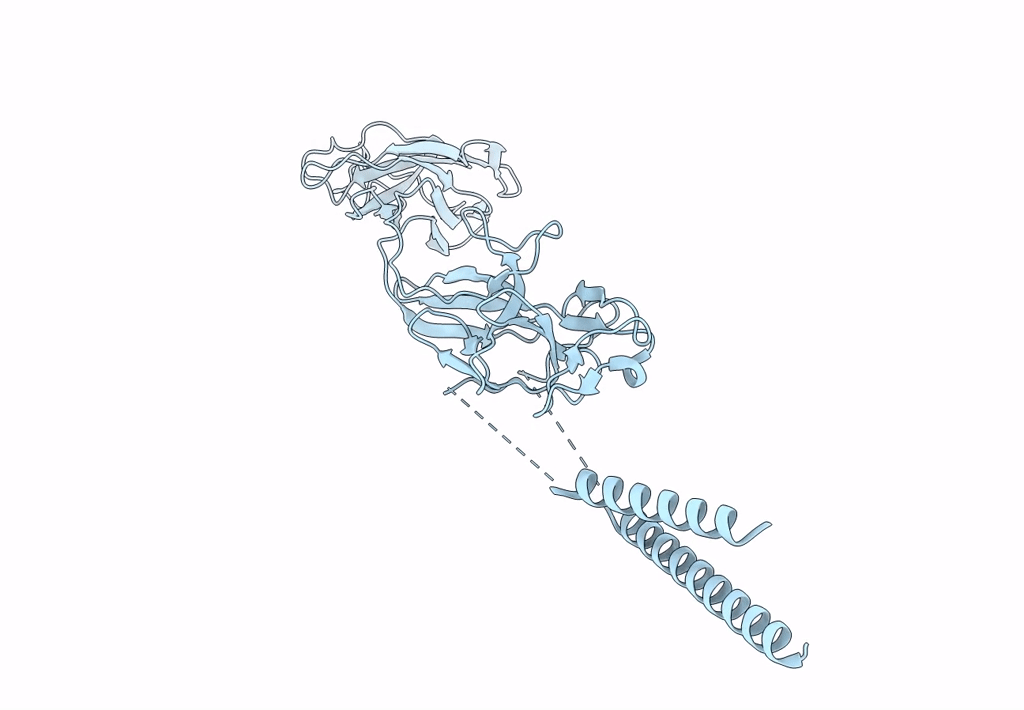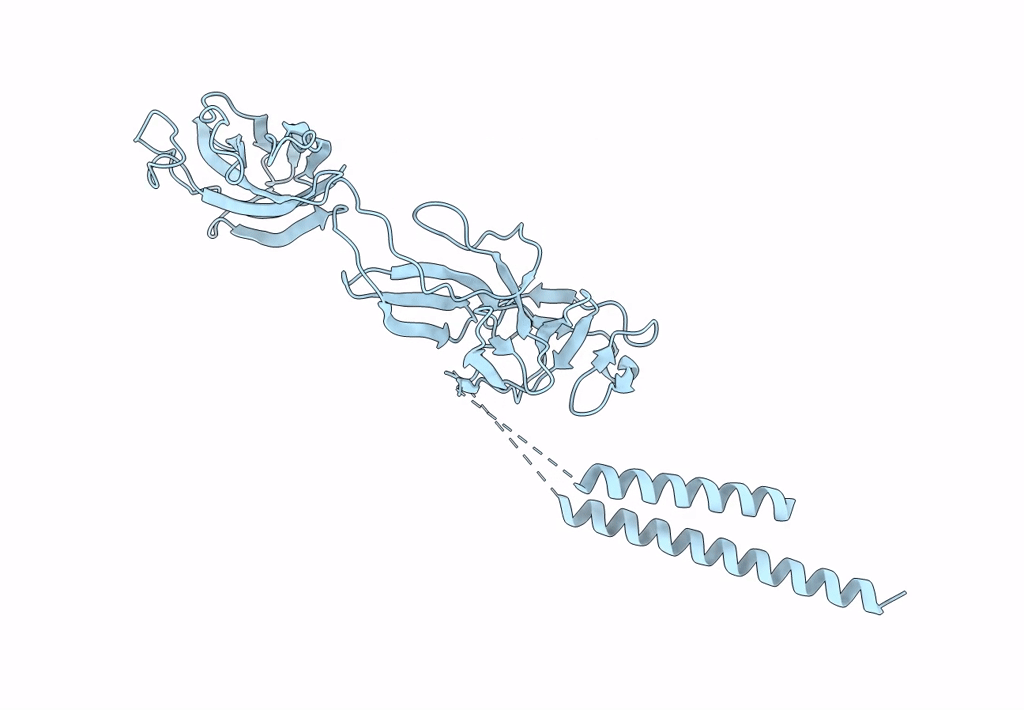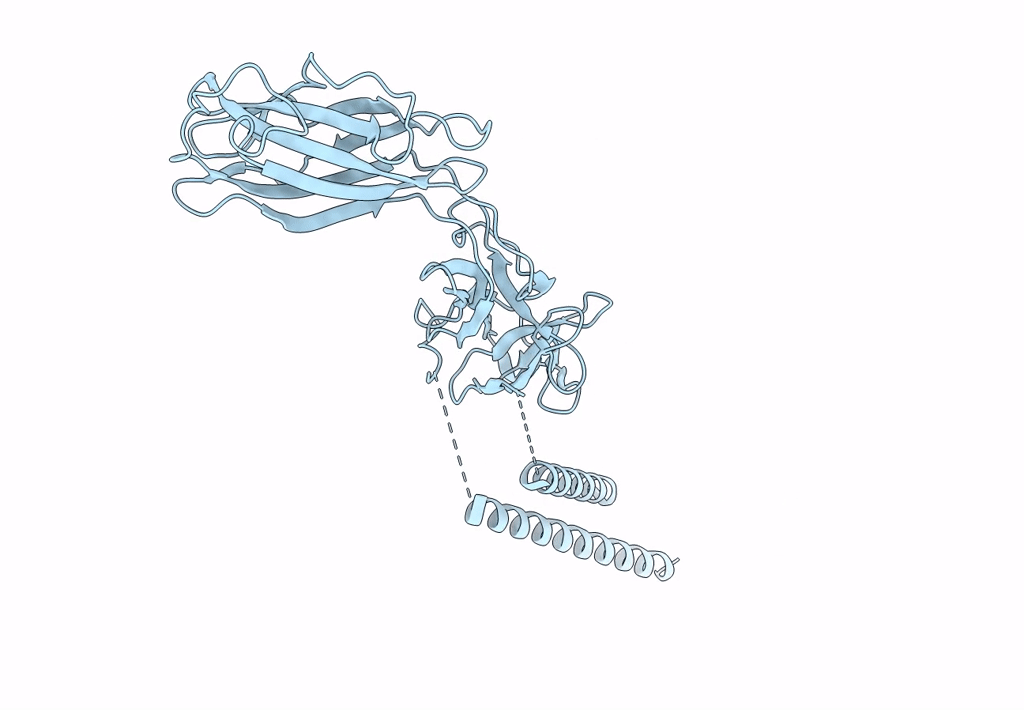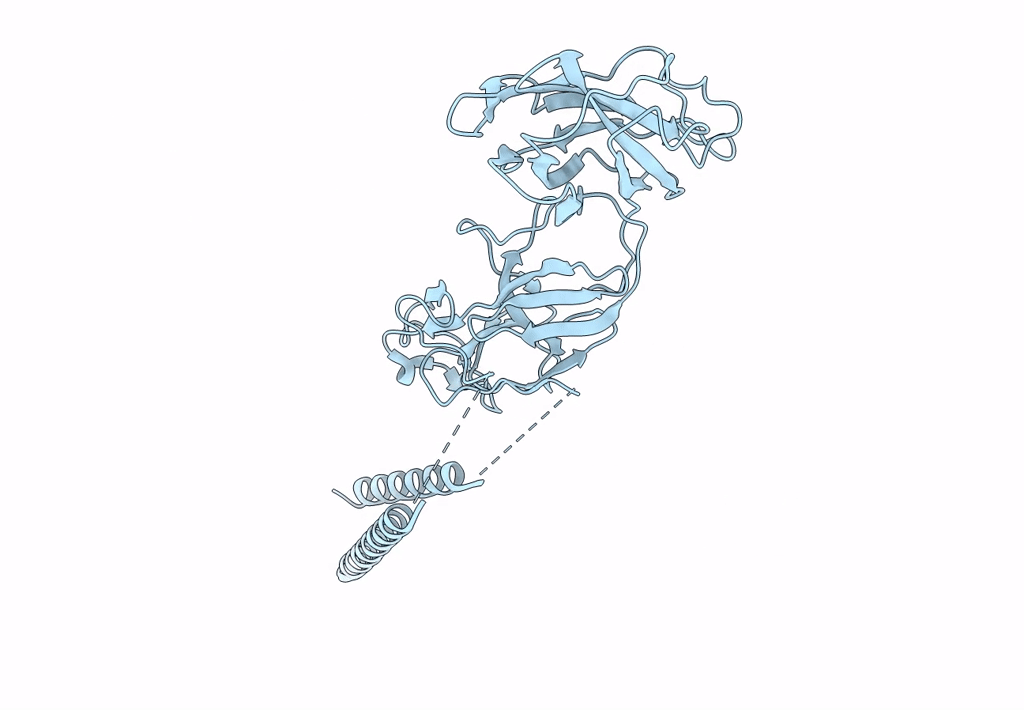
Atomic model of the bacterial flagellar hook based on docking an X-ray derived structure and terminal two alpha-helices into an 7.1 angstrom resolution cryoEM map
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
7.10 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
HELICAL