Deposition Date
2009-02-05
Release Date
2009-03-24
Last Version Date
2023-11-01
Entry Detail
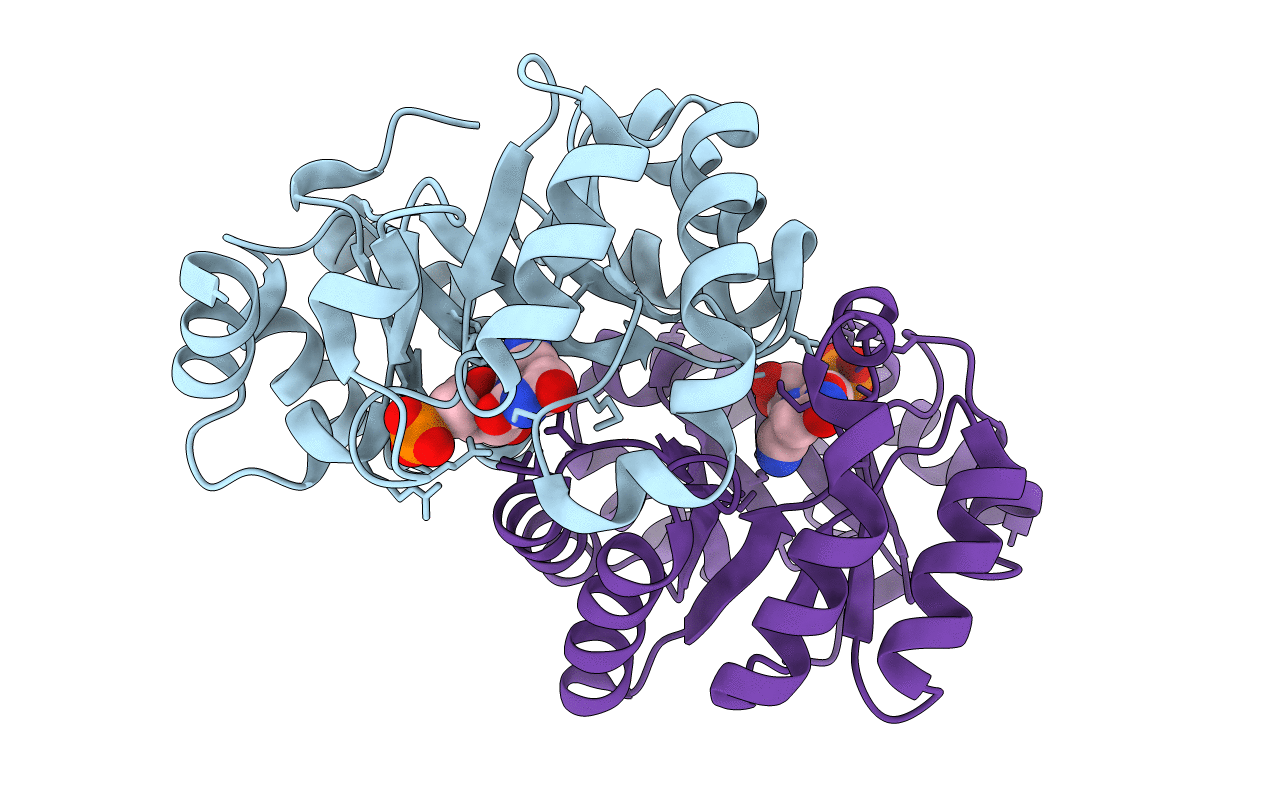
PDB ID:
2ZZ5
Keywords:
Title:
Orotidine Monophosphate Deacarboxylase D70A/K72A double mutant from M. thermoautotrophicum complexed with 6- cyano-UMP
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (Taxon ID: 145262)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.56 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.15
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 1 21 1


