Deposition Date
2010-11-28
Release Date
2011-07-20
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2XZR
Keywords:
Title:
Escherichia coli Immunoglobulin-binding protein EibD 391-438 FUSED TO GCN4 ADAPTORS
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
ENTEROBACTERIA PHAGE P-EIBD (Taxon ID: 120163)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
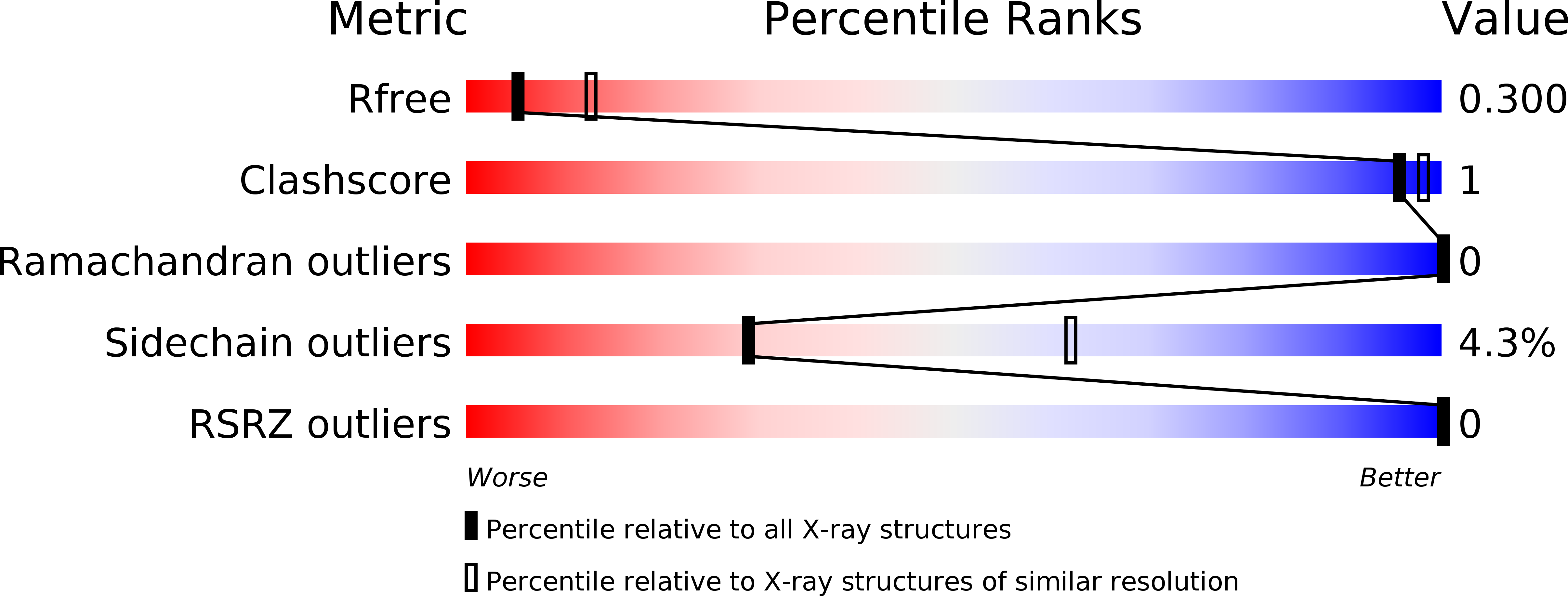
Resolution:
2.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.30
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.26
Space Group:
P 3 2 1