Abstact
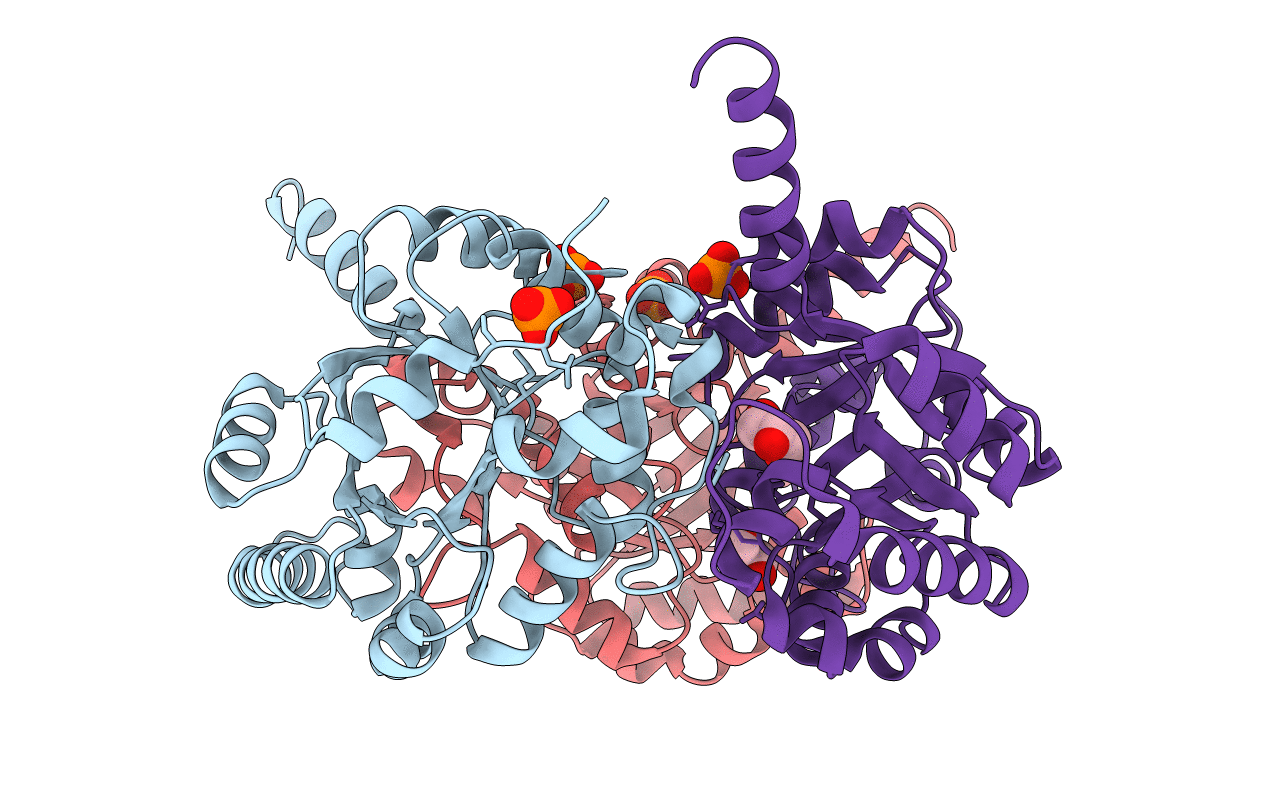
One of the major challenges in the postgenomic era is the functional assignment of proteins using sequence- and structure-based predictive methods coupled with experimental validation. We have used these approaches to investigate the structure and function of the Escherichia coli K-12 protein YfaU, annotated as a putative 4-hydroxy-2-ketoheptane-1,7-dioate aldolase (HpcH) in the sequence databases. HpcH is the final enzyme in the degradation pathway of the aromatic compound homoprotocatechuate. We have determined the crystal structure of apo-YfaU and the Mg (2+)-pyruvate product complex. Despite greater sequence and structural similarity to HpcH, genomic context suggests YfaU is instead a 2-keto-3-deoxy sugar aldolase like the homologous 2-dehydro-3-deoxygalactarate aldolase (DDGA). Enzyme kinetic measurements show activity with the probable physiological substrate 2-keto-3-deoxy- l-rhamnonate, supporting the functional assignment, as well as the structurally similar 2-keto-3-deoxy- l-mannonate and 2-keto-3-deoxy- l-lyxonate (see accompanying paper: Rakus, J. F., Fedorov, A. A., Fedorov, E. V., Glasner, M. E., Hubbard, B. K., Delli, J. D., Babbitt, P. C., Almo, S. C., and Gerlt, J. A. (2008) Biochemistry 47, 9944-9954). YfaU has similar activity toward the HpcH substrate 4-hydroxy-2-ketoheptane-1,7-dioate and synthetic substrates 4-hydroxy-2-ketopentanoic acid and 4-hydroxy-2-ketohexanoic acid. This indicates a relaxed substrate specificity that complicates the functional assignment of members of this enzyme superfamily. Crystal structures suggest these enzymes use an Asp-His intersubunit dyad to activate a metal-bound water or hydroxide for proton transfer during catalysis.