Deposition Date
2008-03-13
Release Date
2008-04-29
Last Version Date
2025-12-17
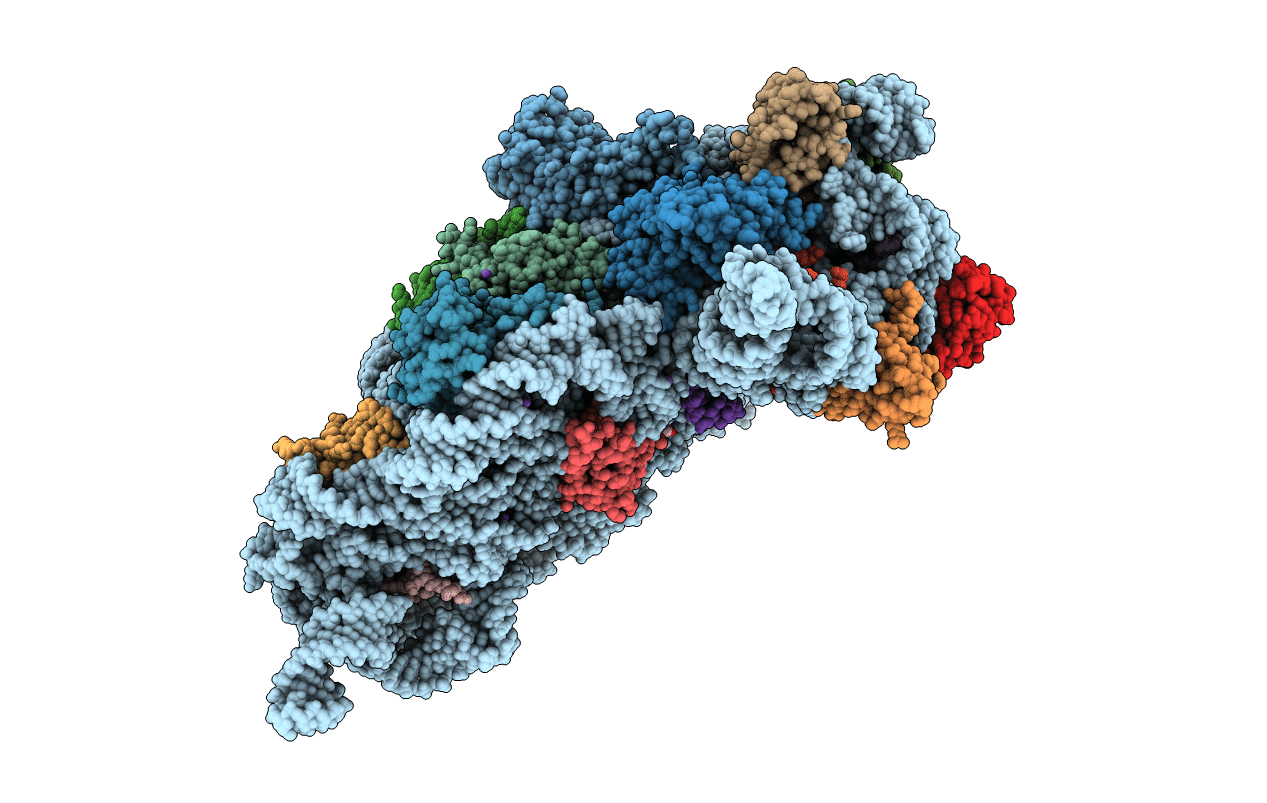
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2VQE
Keywords:
Title:
Modified uridines with C5-methylene substituents at the first position of the tRNA anticodon stabilize U-G wobble pairing during decoding
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
THERMUS THERMOPHILUS (Taxon ID: 300852)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
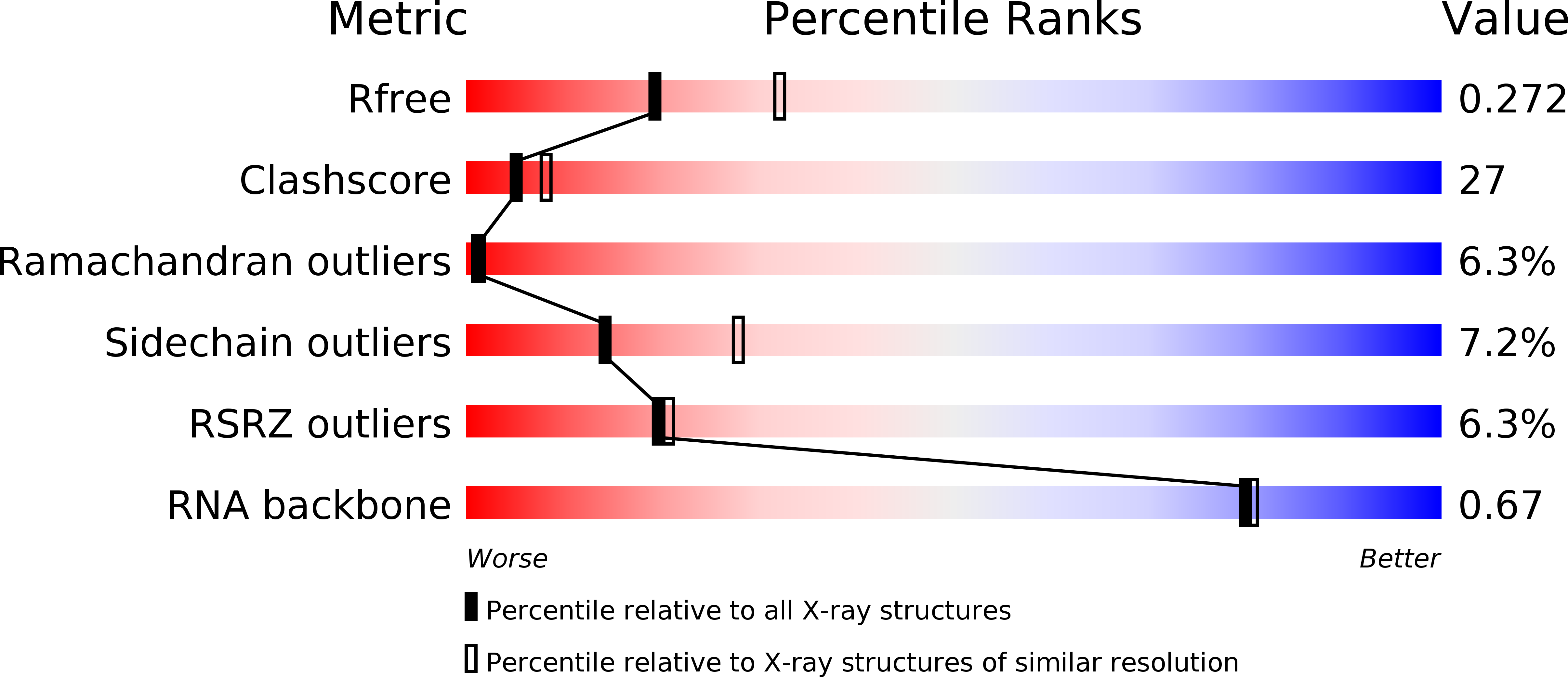
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 41 21 2