Deposition Date
2007-06-05
Release Date
2007-12-25
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
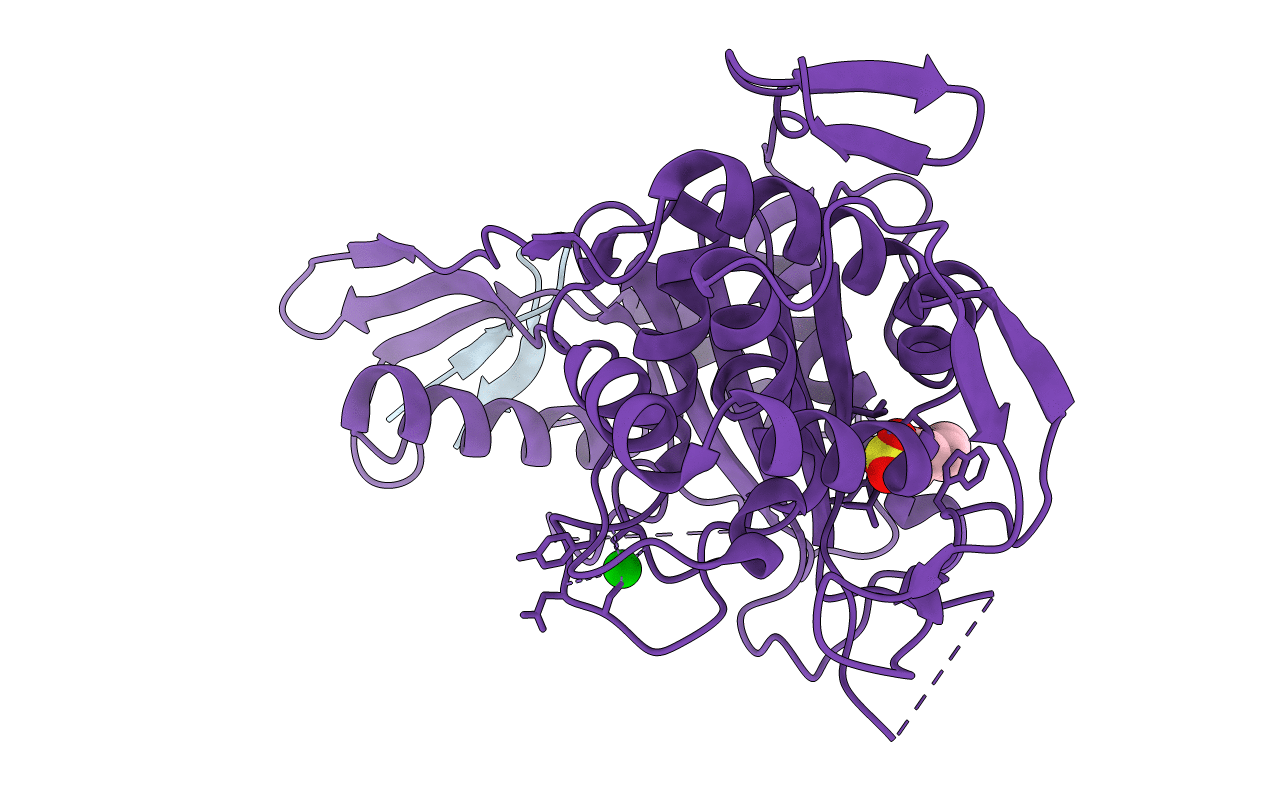
PDB ID:
2V2F
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of PBP1a from drug-resistant strain 5204 from Streptococcus pneumoniae
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE (Taxon ID: 1313)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
C 1 2 1


