Deposition Date
2007-05-14
Release Date
2007-07-03
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2V0C
Keywords:
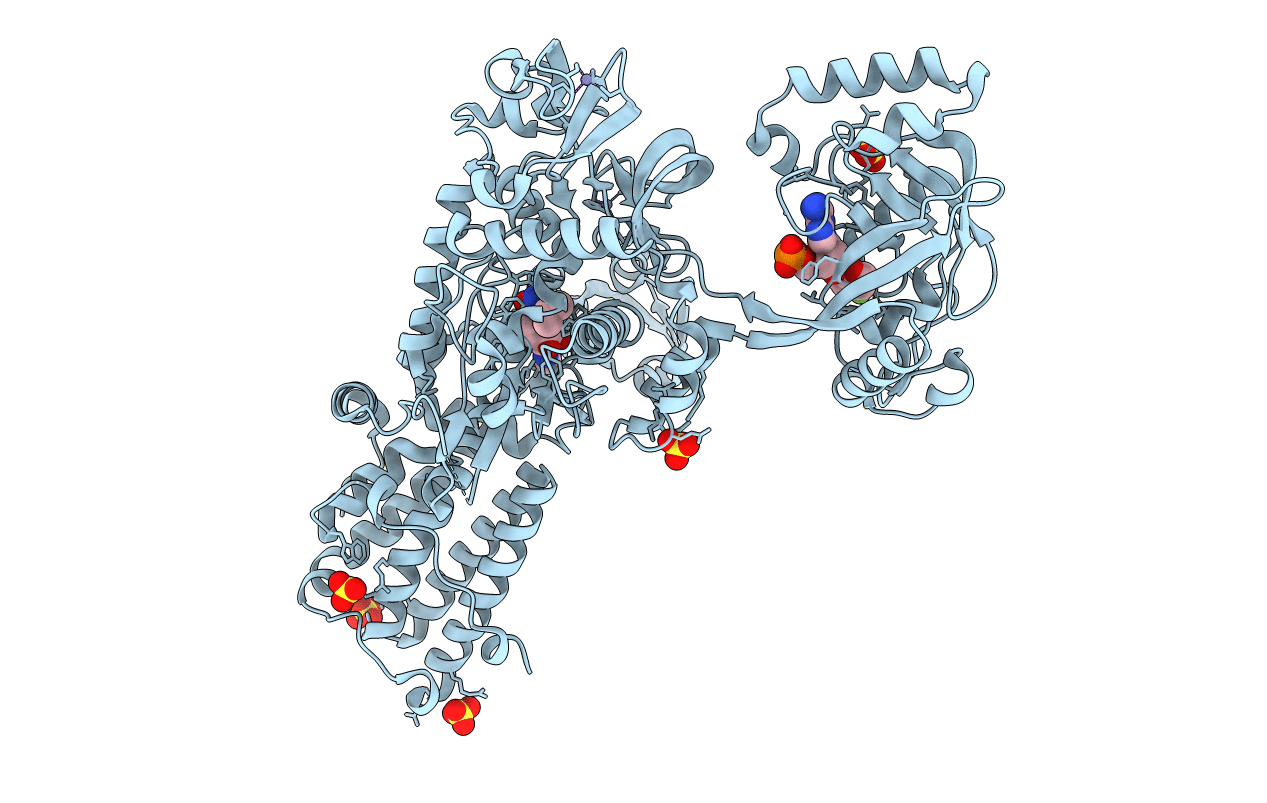
Title:
LEUCYL-TRNA SYNTHETASE FROM THERMUS THERMOPHILUS COMPLEXED WITH A SULPHAMOYL ANALOGUE OF LEUCYL-ADENYLATE In the synthetic site and an adduct of AMP with 5-Fluoro-1,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborole (AN2690) in the editing site
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
THERMUS THERMOPHILUS (Taxon ID: 274)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.85 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
C 2 2 21


