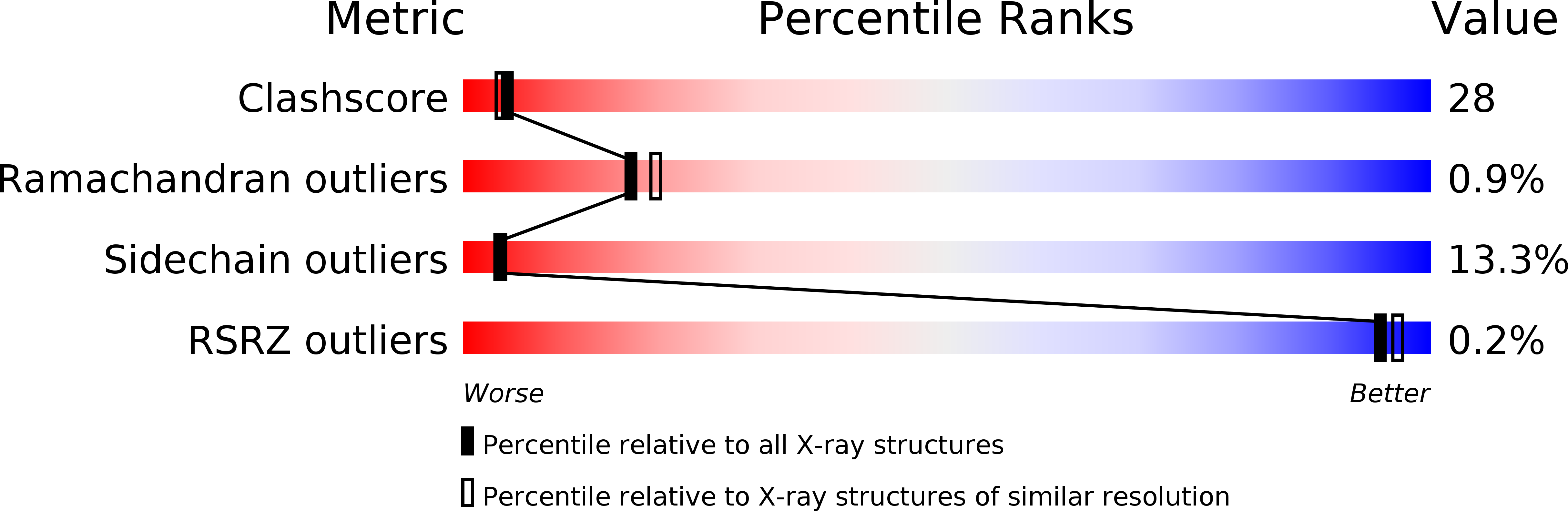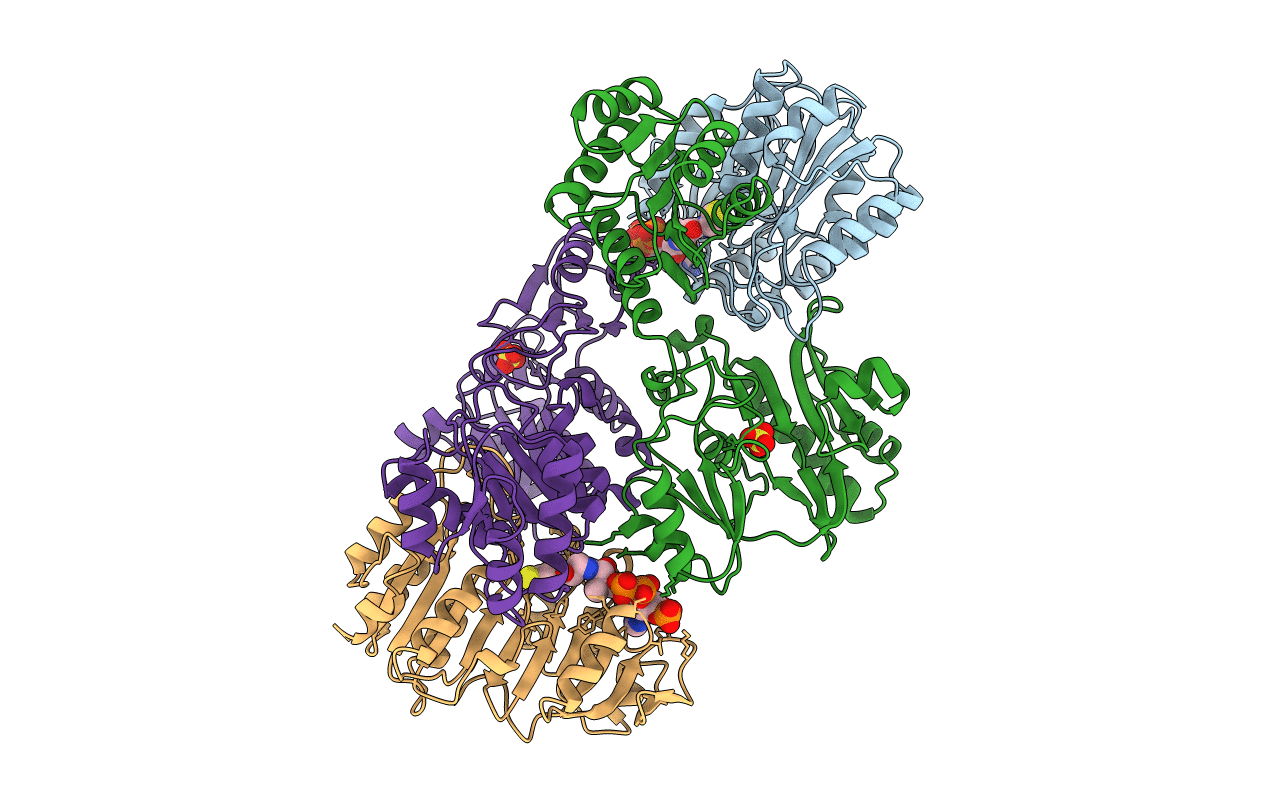
Deposition Date
1998-09-24
Release Date
1999-08-02
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2SCU
Keywords:
Title:
A detailed description of the structure of Succinyl-COA synthetase from Escherichia coli
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details: