Deposition Date
2007-09-26
Release Date
2008-06-03
Last Version Date
2023-10-25
Entry Detail
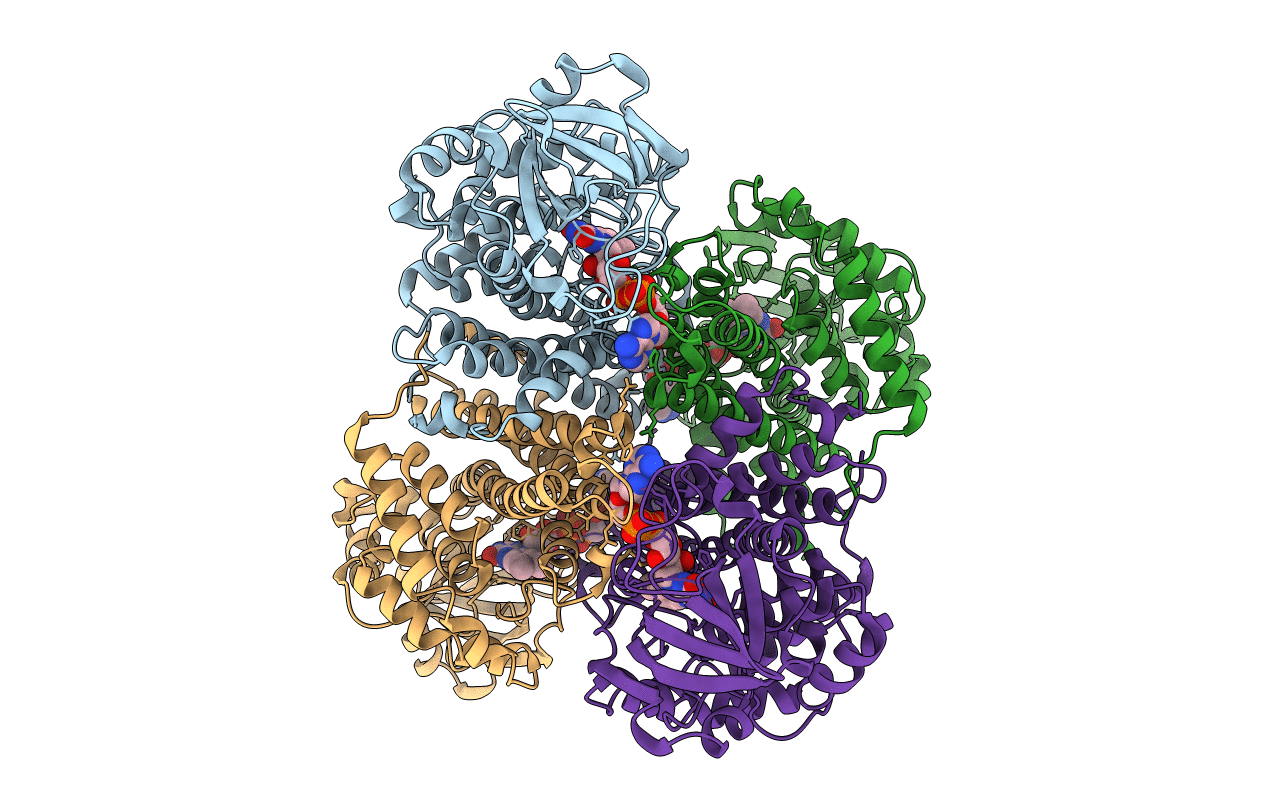
PDB ID:
2REH
Keywords:
Title:
Mechanistic and Structural Analyses of the Roles of Arg409 and Asp402 in the Reaction of the Flavoprotein Nitroalkane Oxidase
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Fusarium oxysporum (Taxon ID: )
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
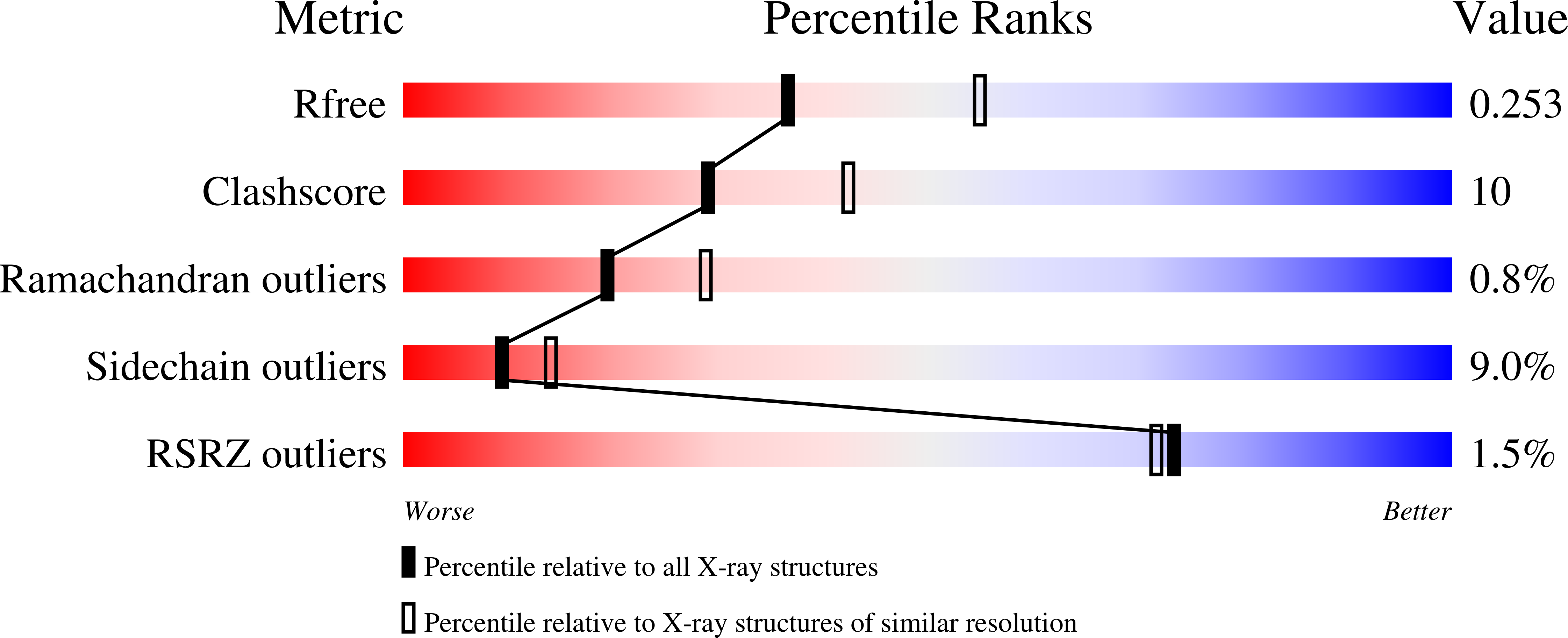
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 32 2 1


