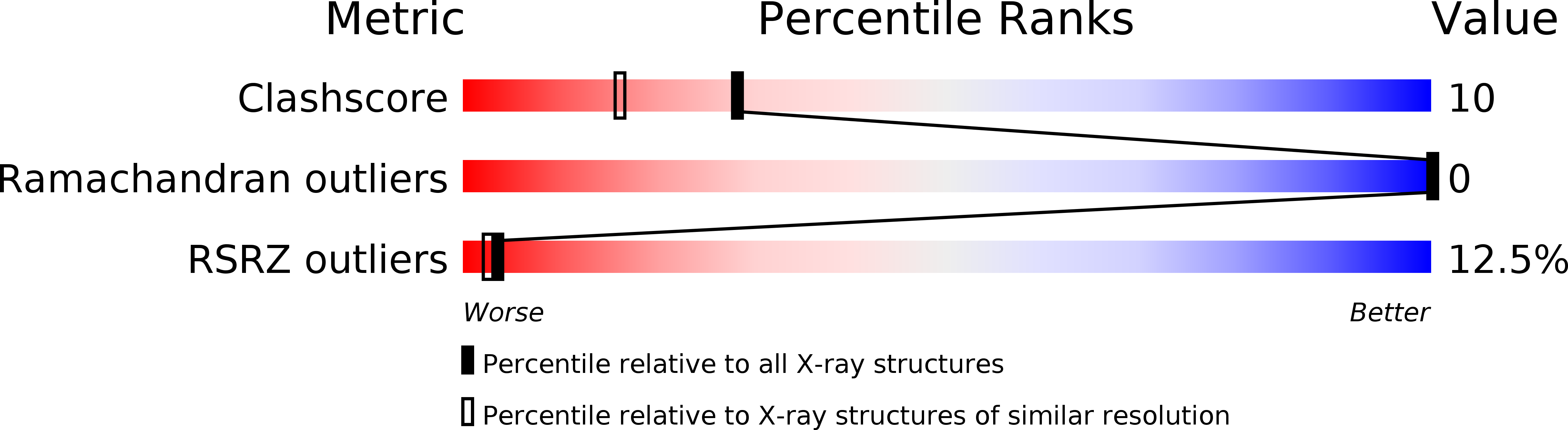
Deposition Date
2007-05-29
Release Date
2007-11-13
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2Q33
Keywords:
Title:
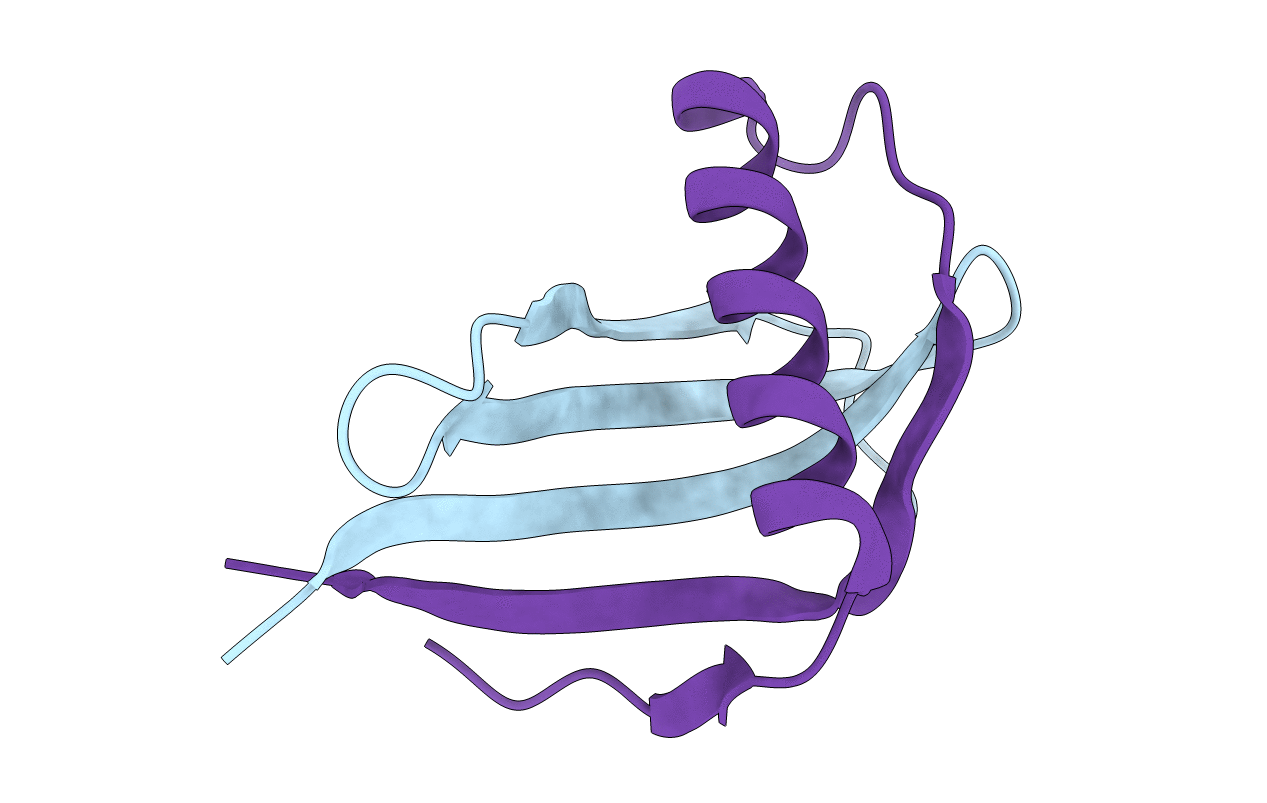
Crystal structure of all-D monellin at 1.8 A resolution
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 1 2 1