Deposition Date
2007-04-24
Release Date
2008-02-26
Last Version Date
2023-08-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2PNC
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of Bovine Plasma Copper-Containing Amine Oxidase in Complex with Clonidine
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
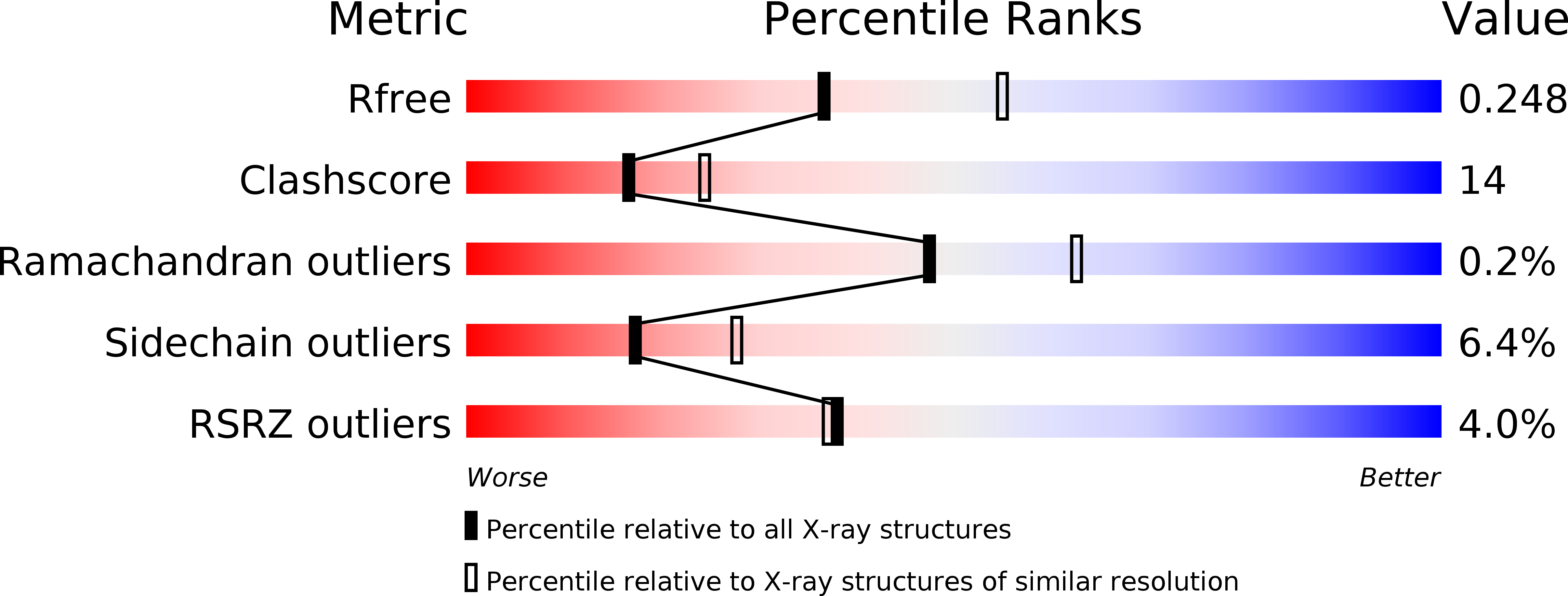
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
P 21 21 21