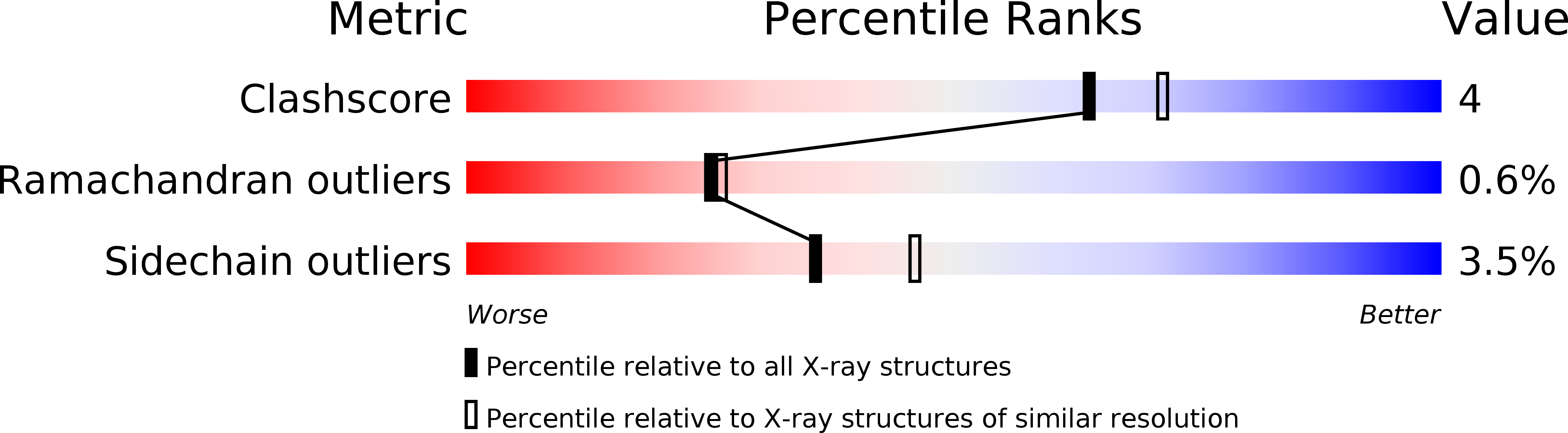Deposition Date
1994-08-08
Release Date
1995-02-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2PEC
Keywords:
Title:
THE REFINED THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF PECTATE LYASE C FROM ERWINIA CHRYSANTHEMI AT 2.2 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION: IMPLICATIONS FOR AN ENZYMATIC MECHANISM
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Erwinia chrysanthemi (Taxon ID: 556)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21