Deposition Date
2007-03-22
Release Date
2007-05-22
Last Version Date
2024-04-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2P8R
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of C. elegans pre-mRNA splicing factor Prp8 carrying R2303K mutant
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Caenorhabditis elegans (Taxon ID: 6239)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
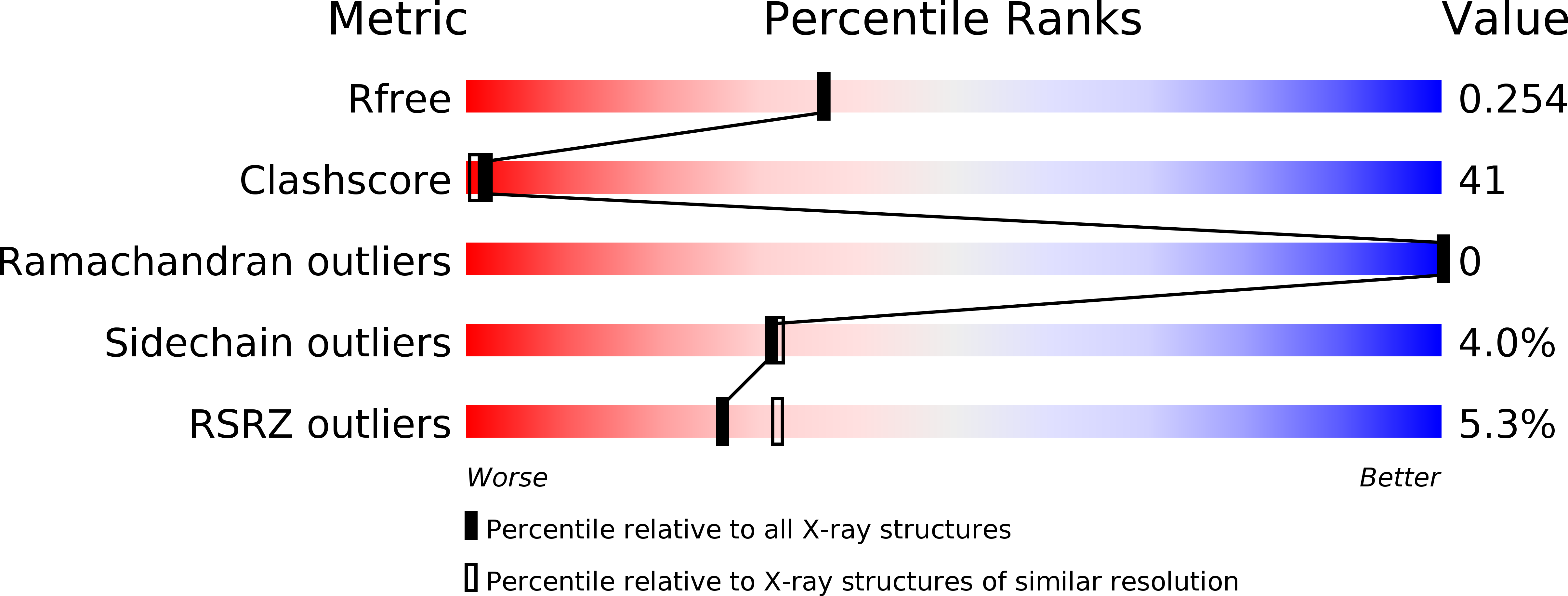
Resolution:
2.10 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.23
Space Group:
P 41 21 2