Deposition Date
2006-12-18
Release Date
2007-01-23
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2OB7
Keywords:
Title:
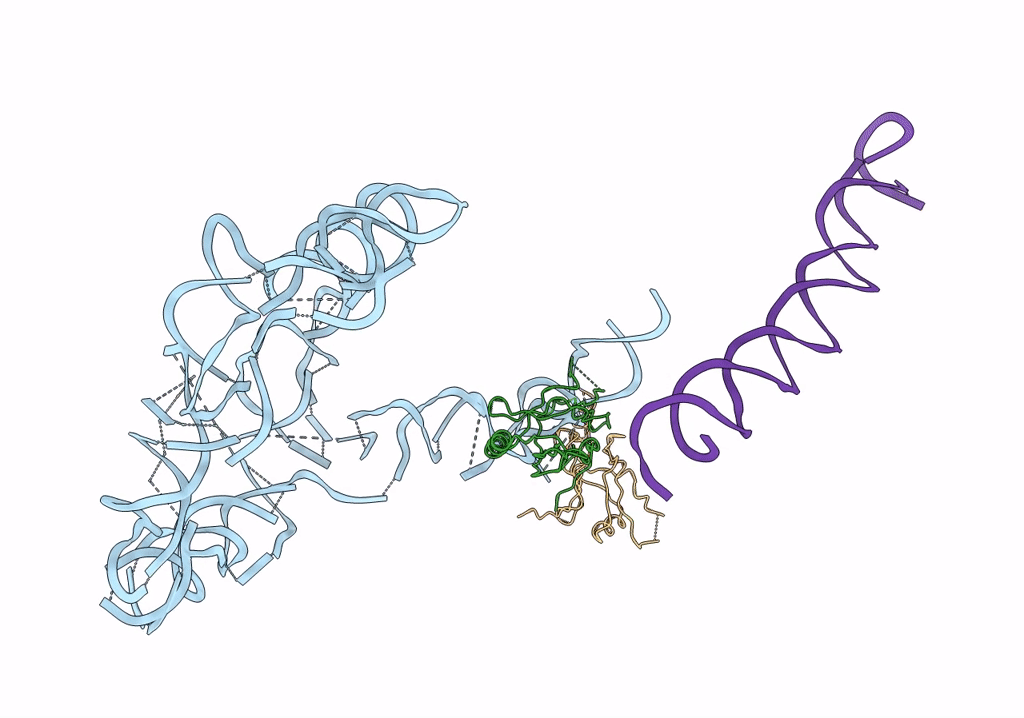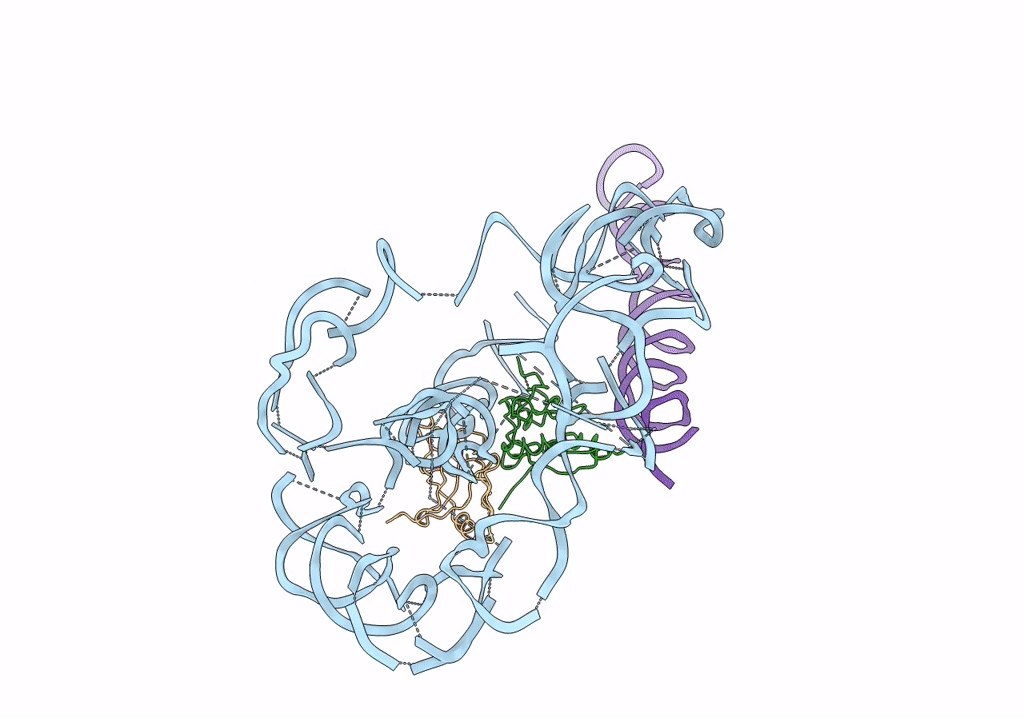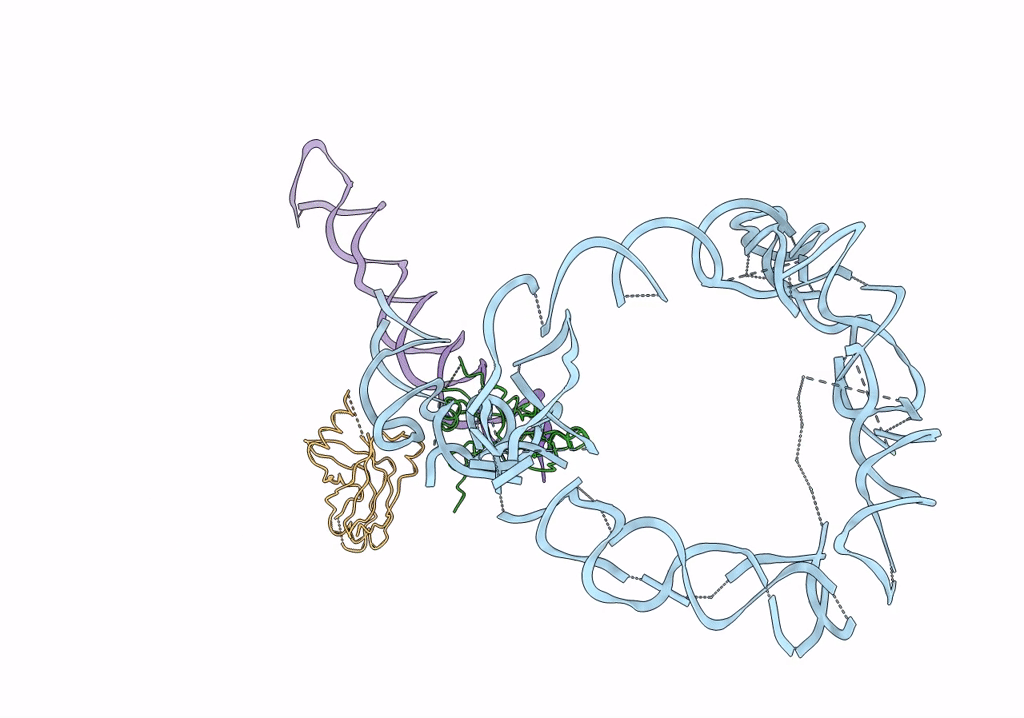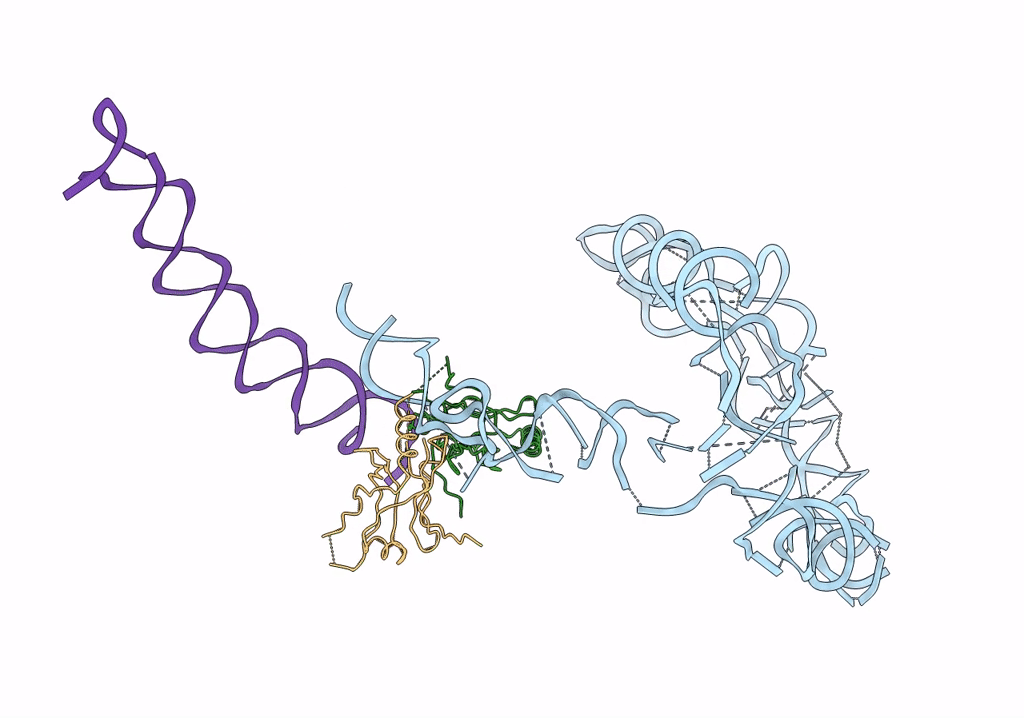
Structure of tmRNA-(SmpB)2 complex as inferred from cryo-EM
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 274)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
13.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


