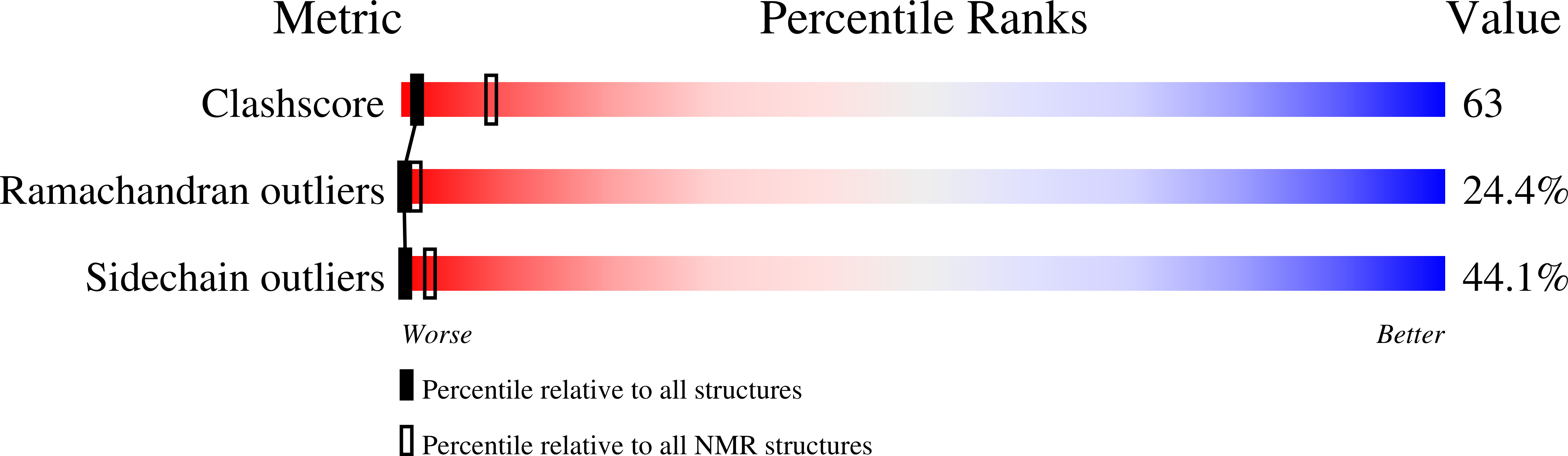
Deposition Date
2006-11-27
Release Date
2007-06-05
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2O00
Keywords:
Title:
NMR structure analysis of the Penetratin conjugated Gas (374-394) peptide
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
24
Conformers Submitted:
24
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted