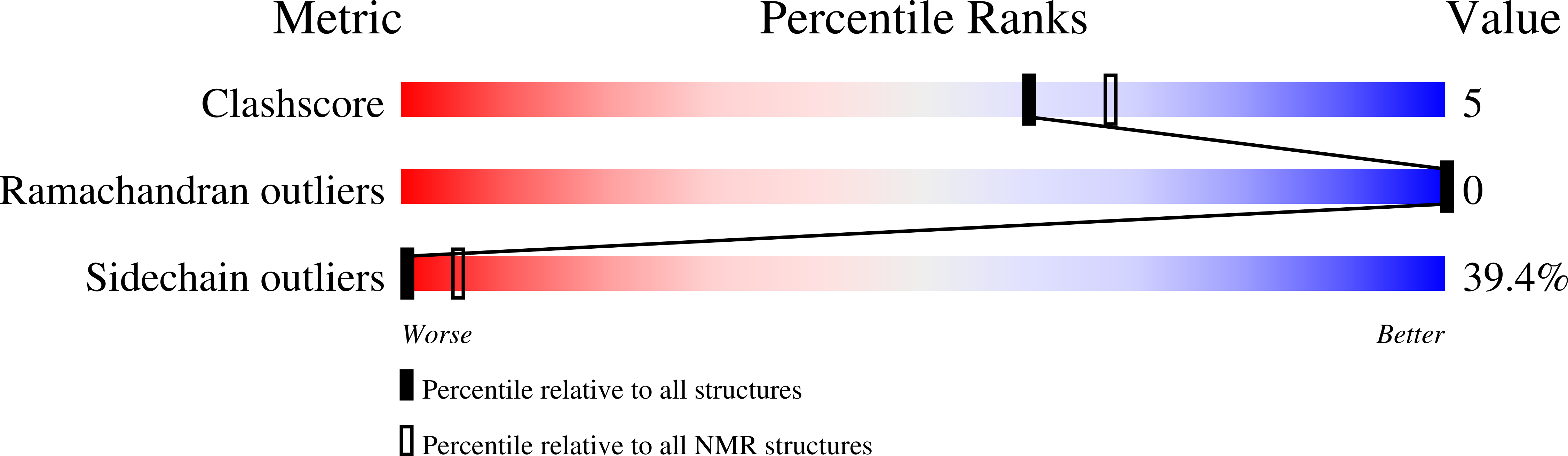
Deposition Date
2006-10-26
Release Date
2006-11-14
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2NOU
Keywords:
Title:
Membrane induced structure of Scyliorhinin I: A Dual NK1/NK2 agonist
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations