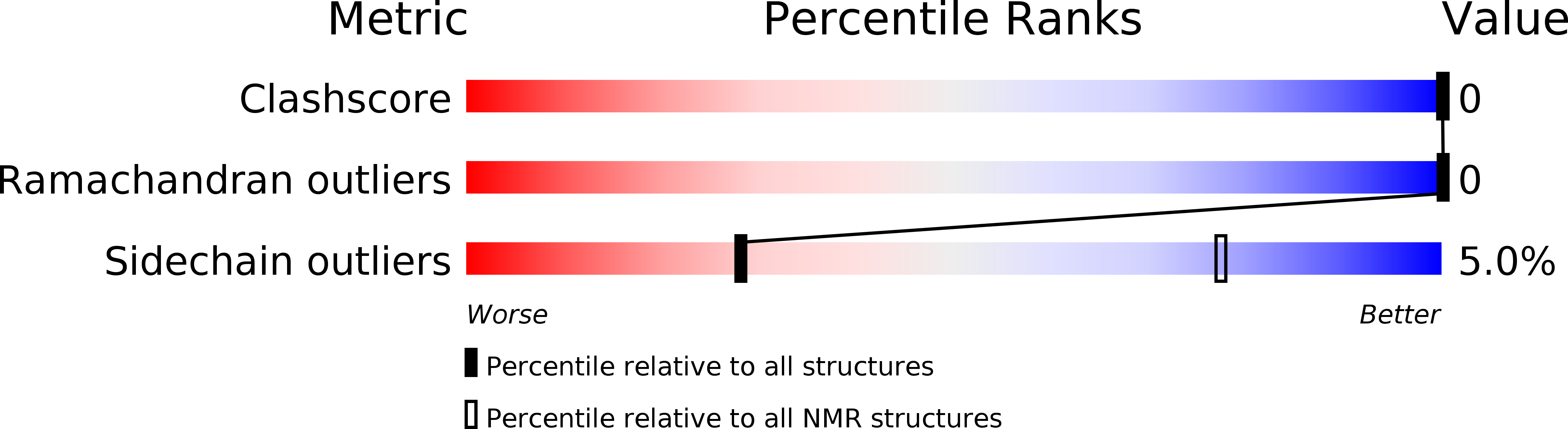
Deposition Date
2016-02-03
Release Date
2017-01-11
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2NBC
Keywords:
Title:
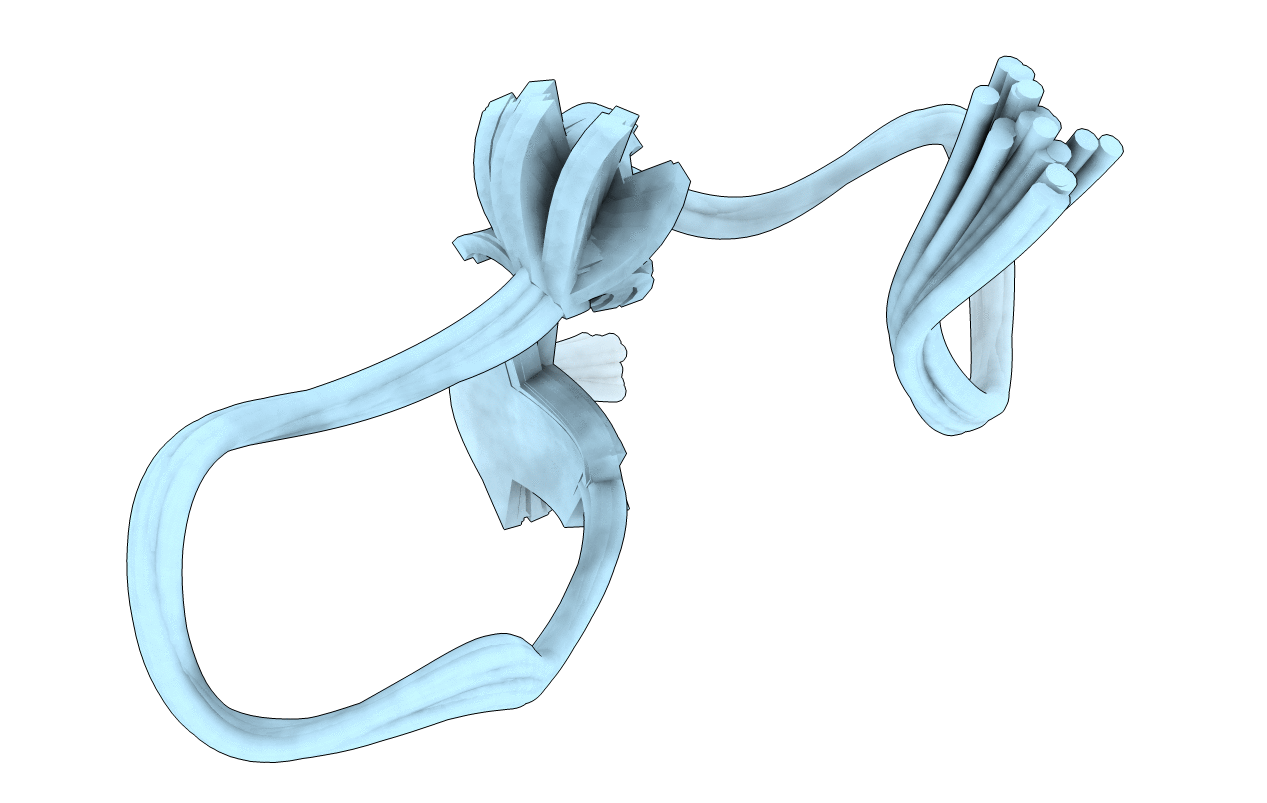
Resonance assignments and structure determination of poneritoxin, omega-PONTX-Ae1a, from Anochetus emarginatus
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Anochetus emarginatus (Taxon ID: 486636)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
30
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
Best stereochemical property judged by Molprobity