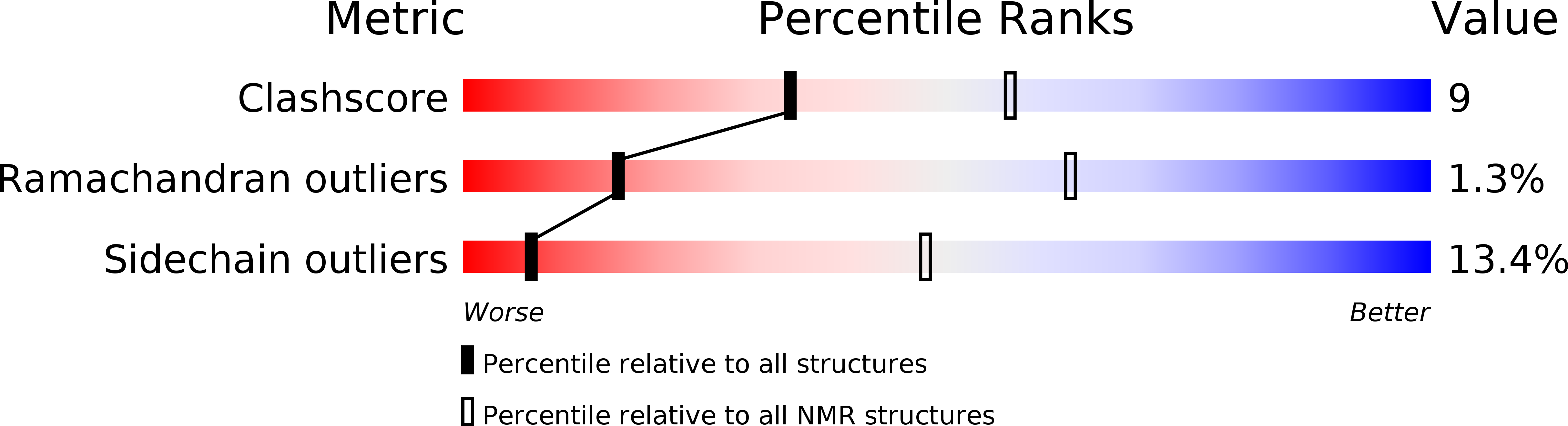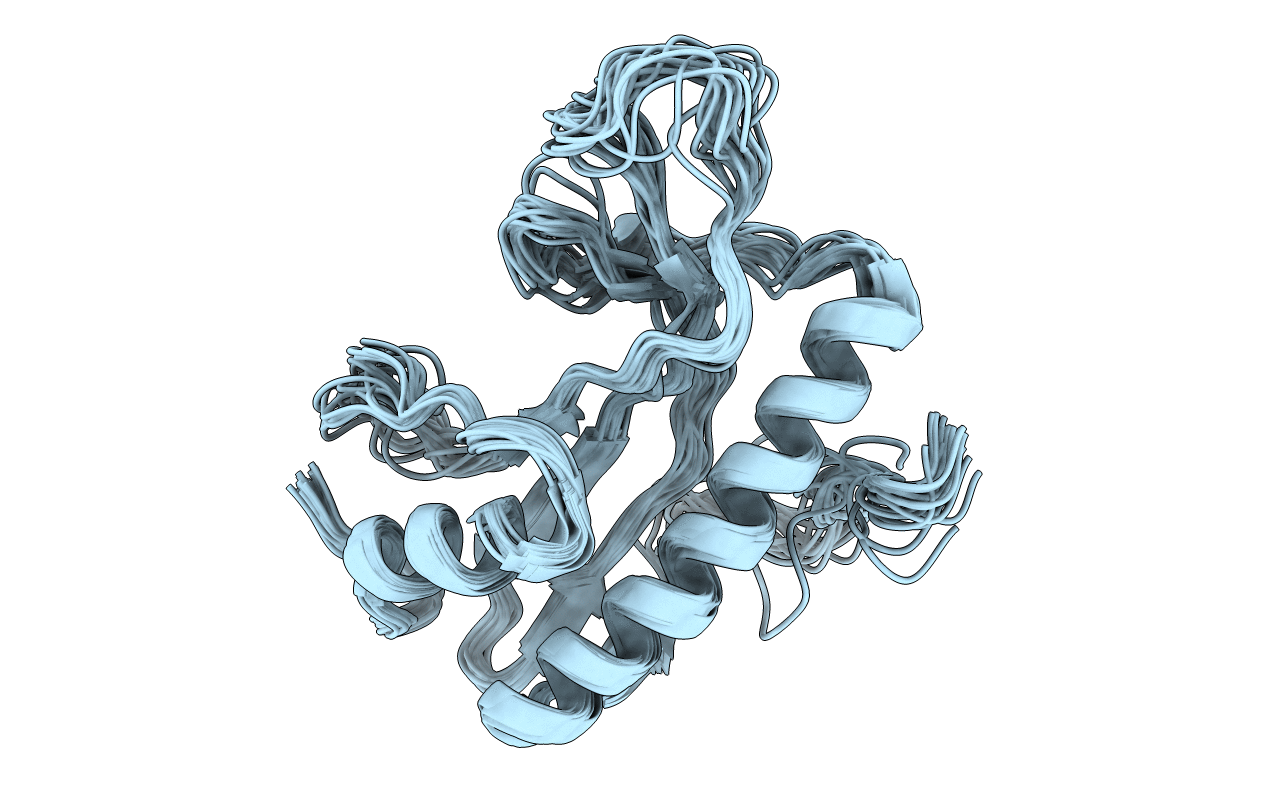
Deposition Date
2015-02-07
Release Date
2015-12-23
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2MZ8
Keywords:
Title:
Solution NMR structure of Salmonella Typhimurium transcriptional regulator protein Crl
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy