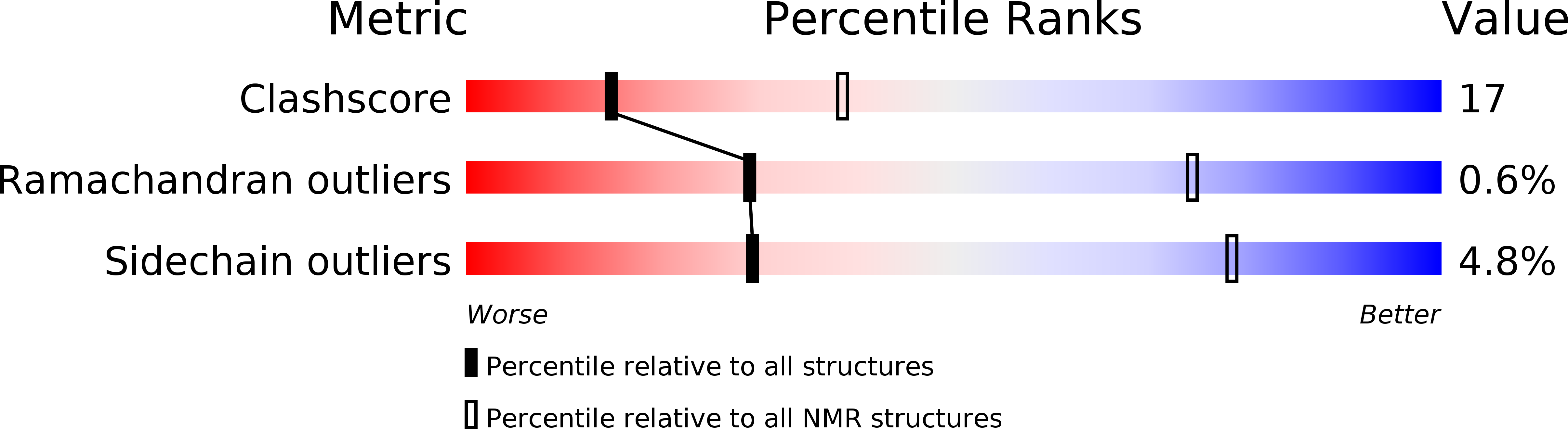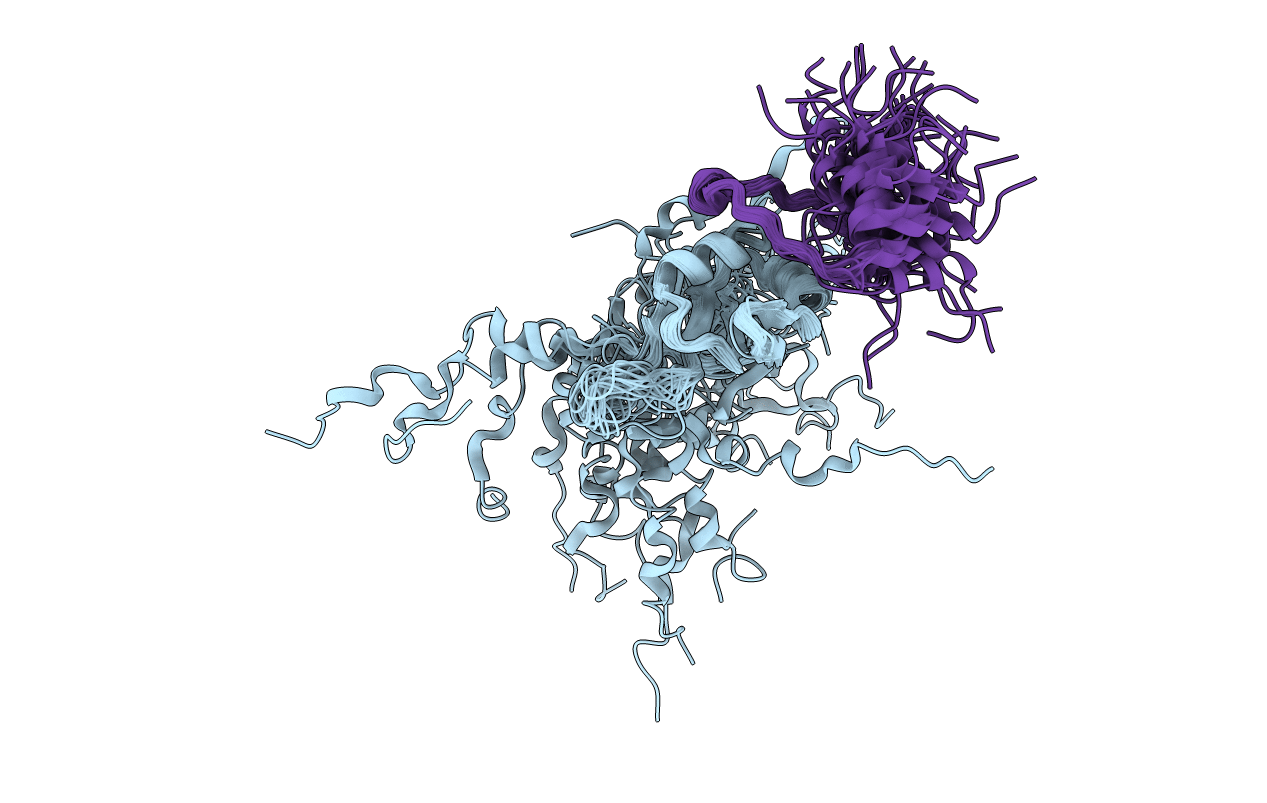
Deposition Date
2015-01-19
Release Date
2015-08-12
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2MY2
Keywords:
Title:
Snu17p-Bud13p structure intermediate during RES complex assembly
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 559292)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
target function