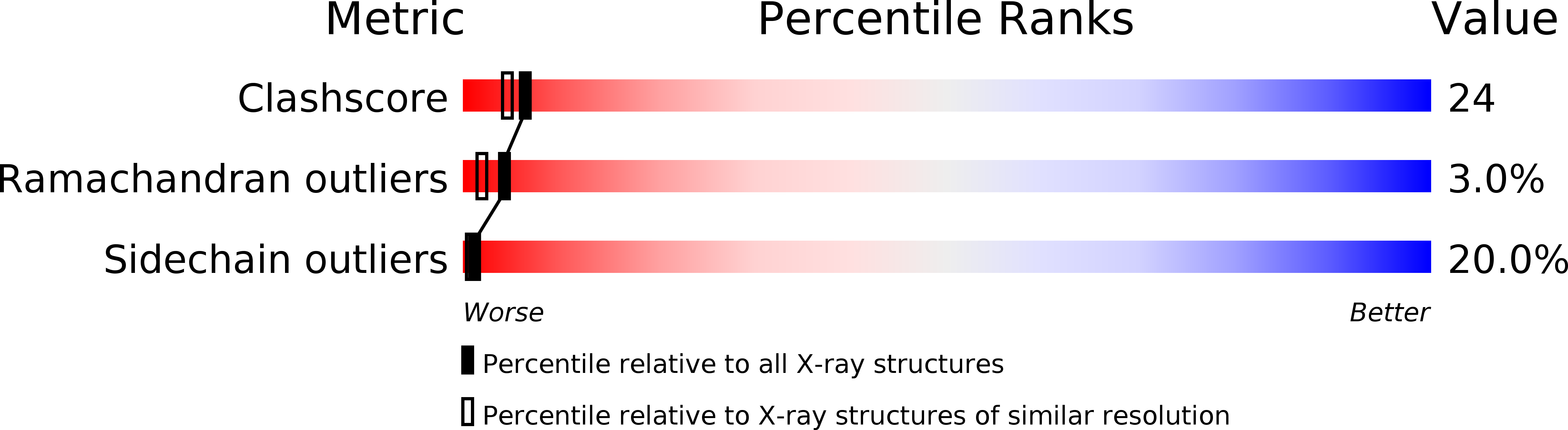Deposition Date
1999-01-27
Release Date
2000-01-28
Last Version Date
2023-12-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2MJP
Keywords:
Title:
STRUCTURE-BASED IDENTIFICATION OF THE BIOCHEMICAL FUNCTION OF A HYPOTHETICAL PROTEIN FROM METHANOCOCCUS JANNASCHII:MJ0226
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Methanocaldococcus jannaschii (Taxon ID: 2190)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.20
Space Group:
P 21 21 21