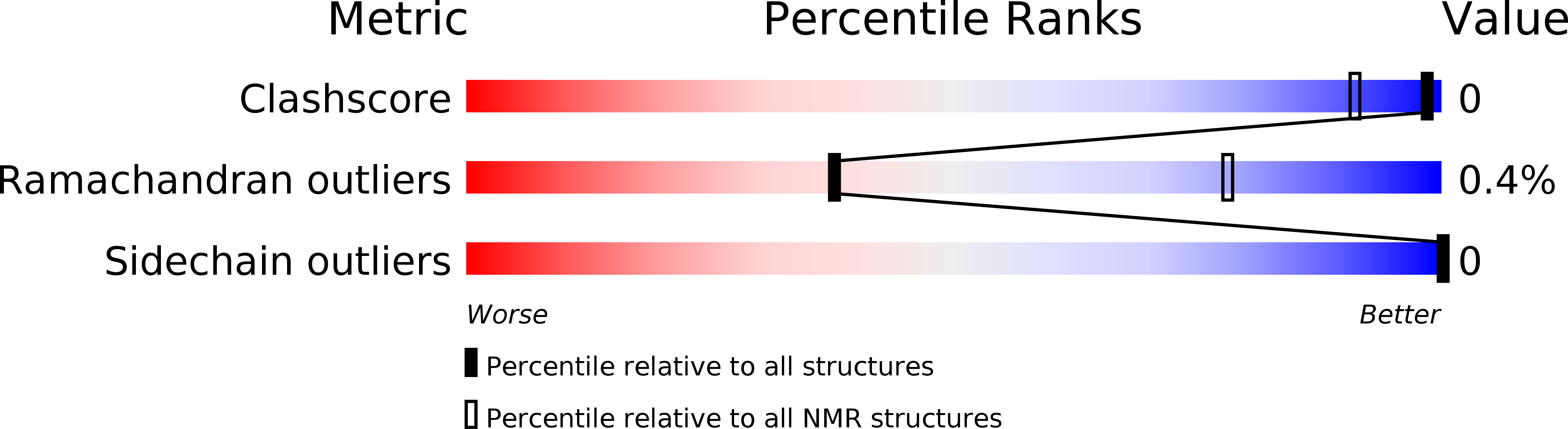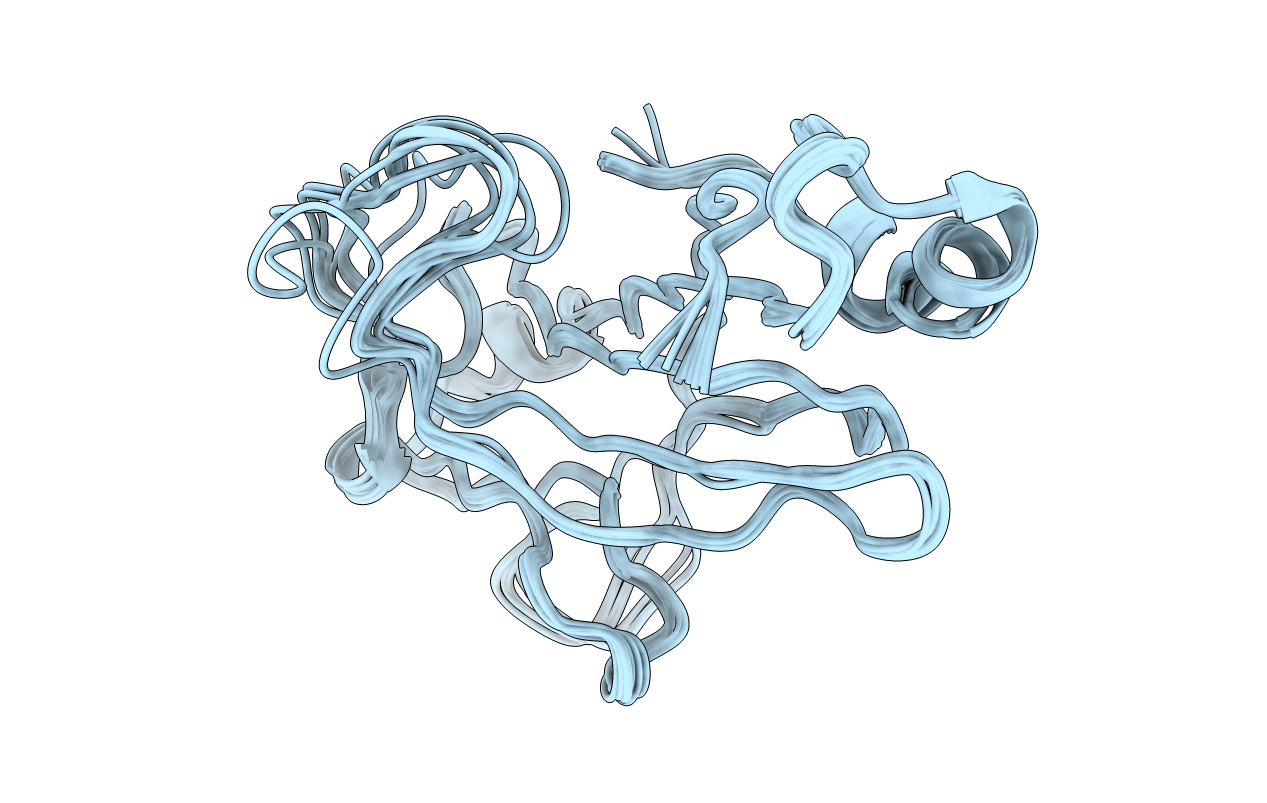
Deposition Date
2013-12-21
Release Date
2014-07-16
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2MIZ
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of the m04/gp34 mouse Cytomegalovirus Immunoevasin core domain
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Murine cytomegalovirus (Taxon ID: 69156)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
10000
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
target function