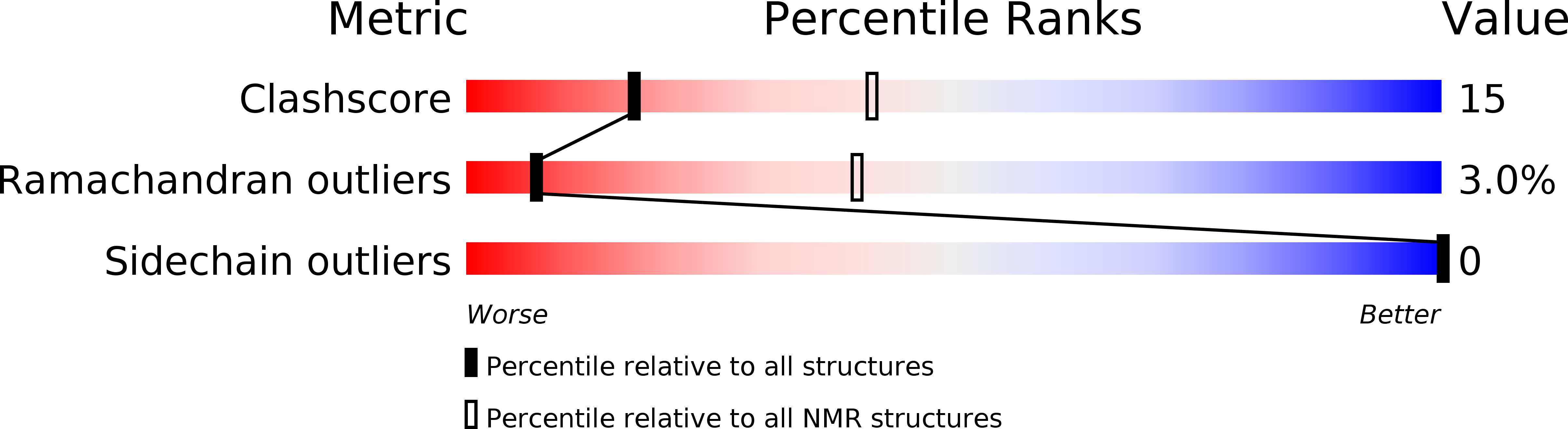
Deposition Date
2013-04-29
Release Date
2014-02-19
Last Version Date
2023-06-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2M7R
Keywords:
Title:
Nmda receptor antagonist, conantokin bk-b, nmr, 20 structure
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
1000
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy