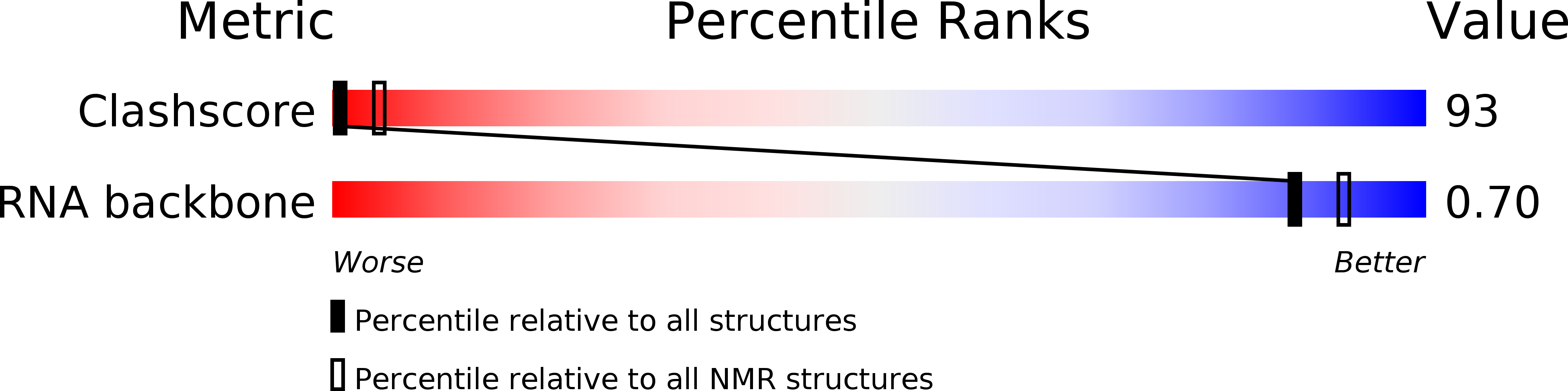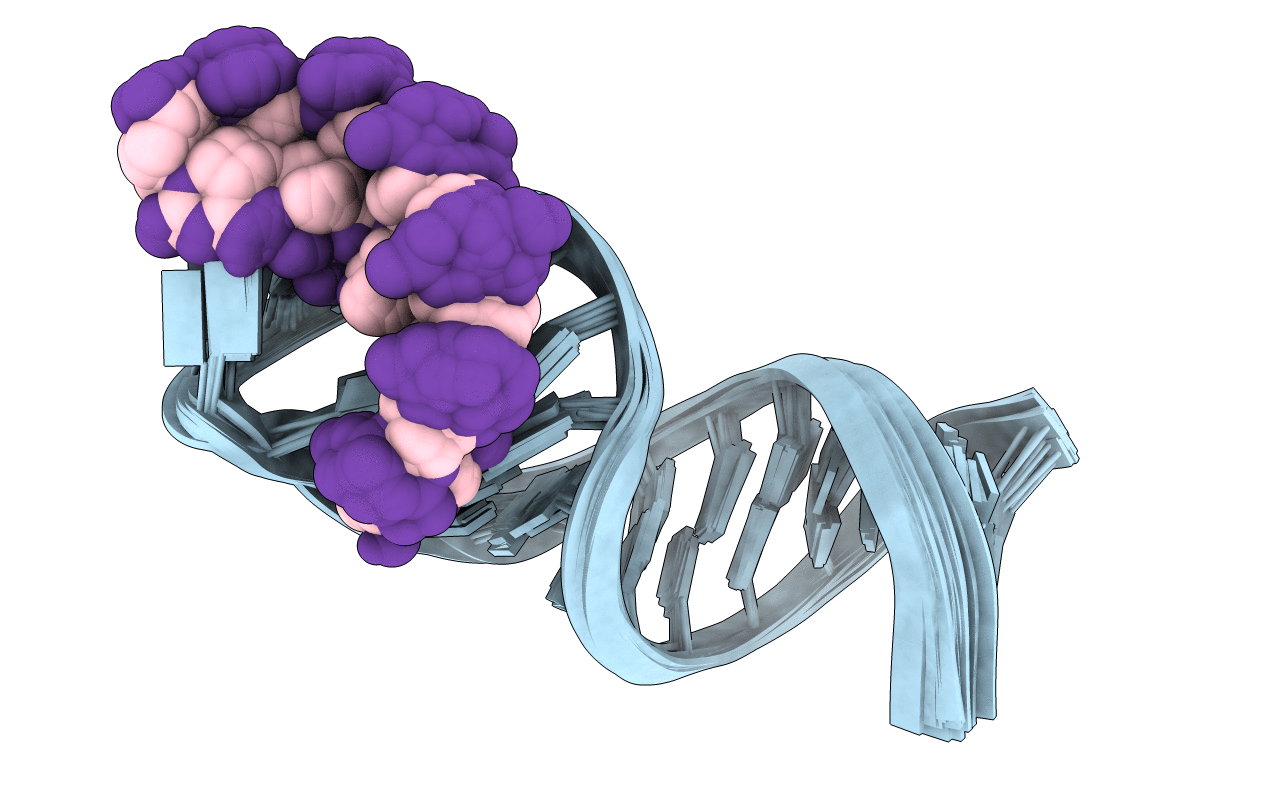
Deposition Date
2012-12-07
Release Date
2014-06-11
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2M1V
Keywords:
Title:
NMR solution structure of the d3'-hairpin from the Sc.ai5gamma group II intron including the EBS1:dIBS1 RNA:DNA hybrid
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
18
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy