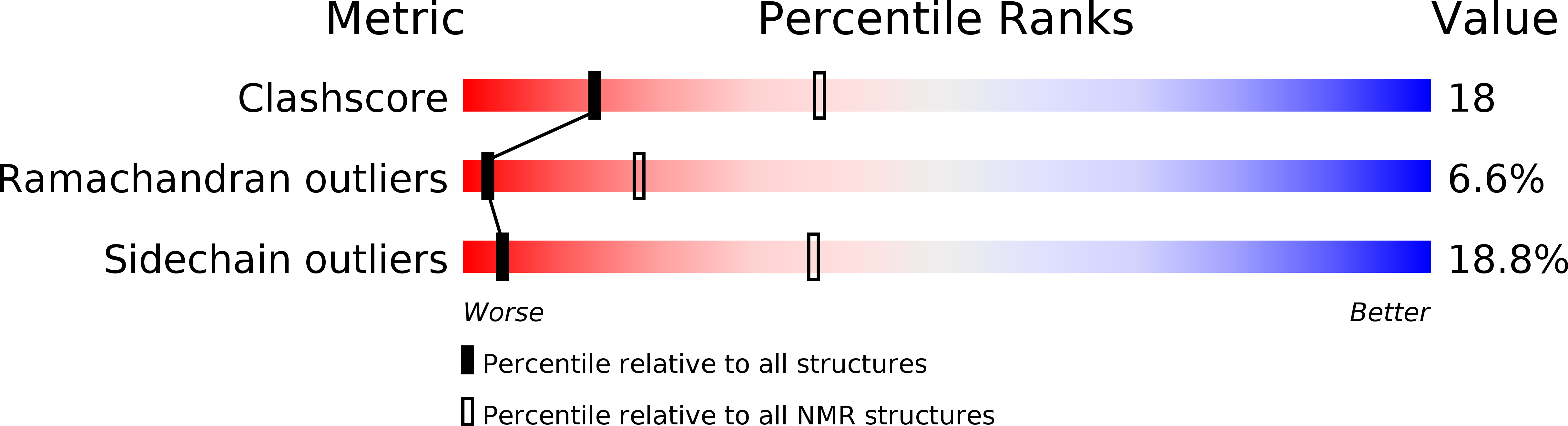
Deposition Date
2012-05-30
Release Date
2013-02-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2LTQ
Keywords:
Title:
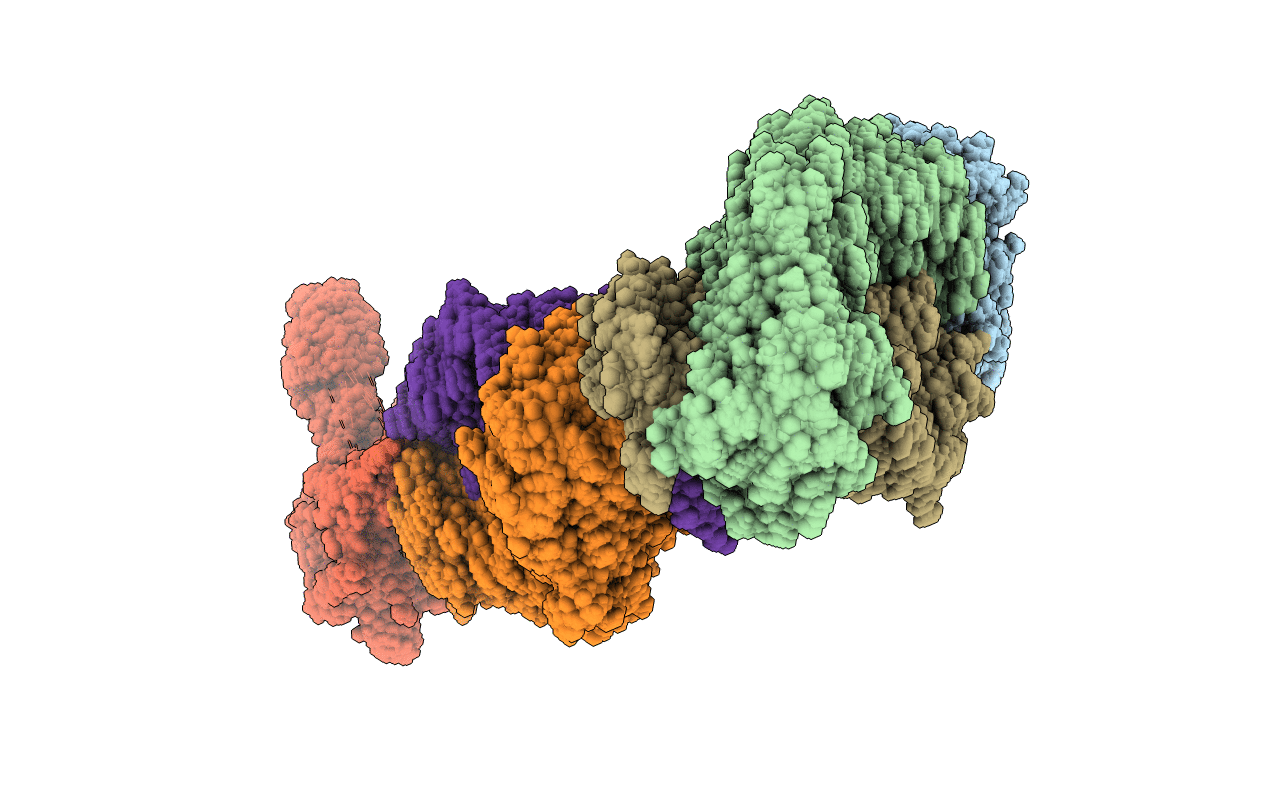
High resolution structure of DsbB C41S by joint calculation with solid-state NMR and X-ray data
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy