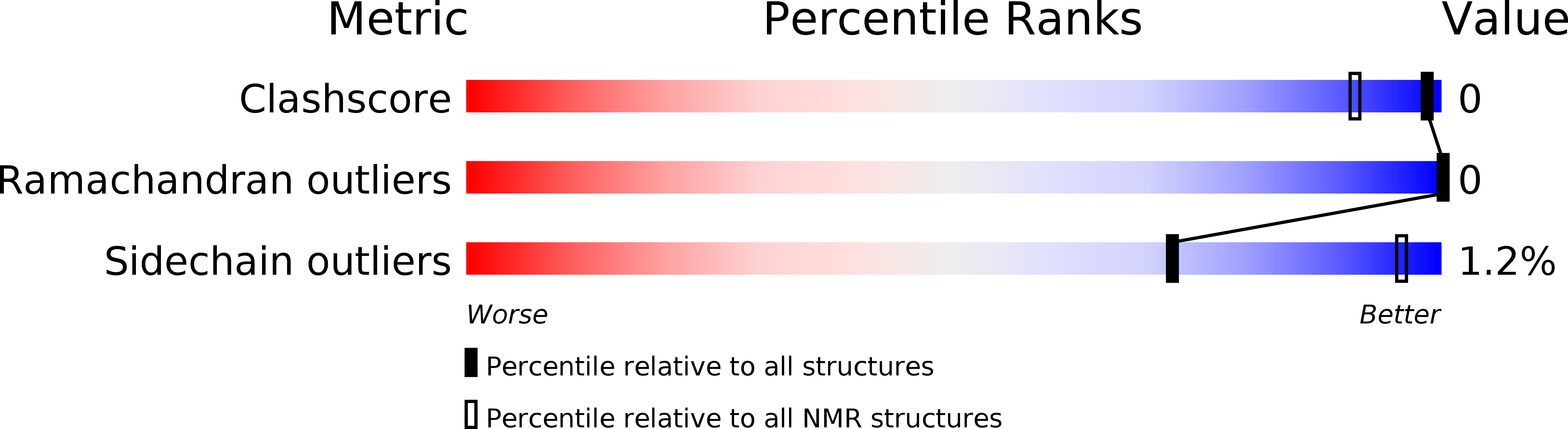Deposition Date
2010-01-07
Release Date
2011-01-19
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Tegenaria agrestis (Taxon ID: 73900)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
25
Selection Criteria:
BEST MOLPROBITY SCORE