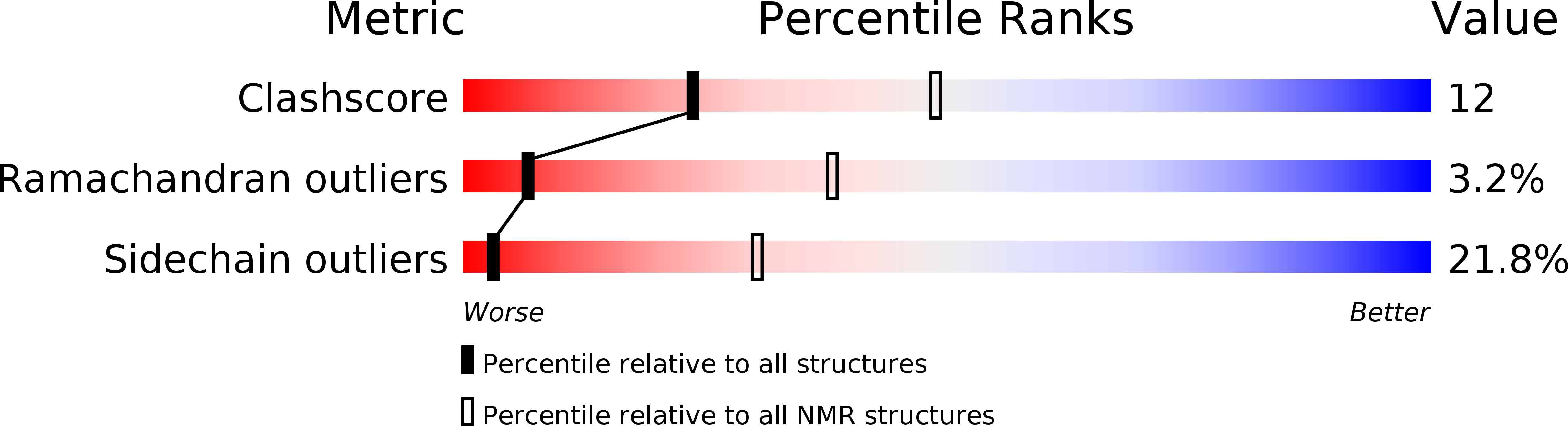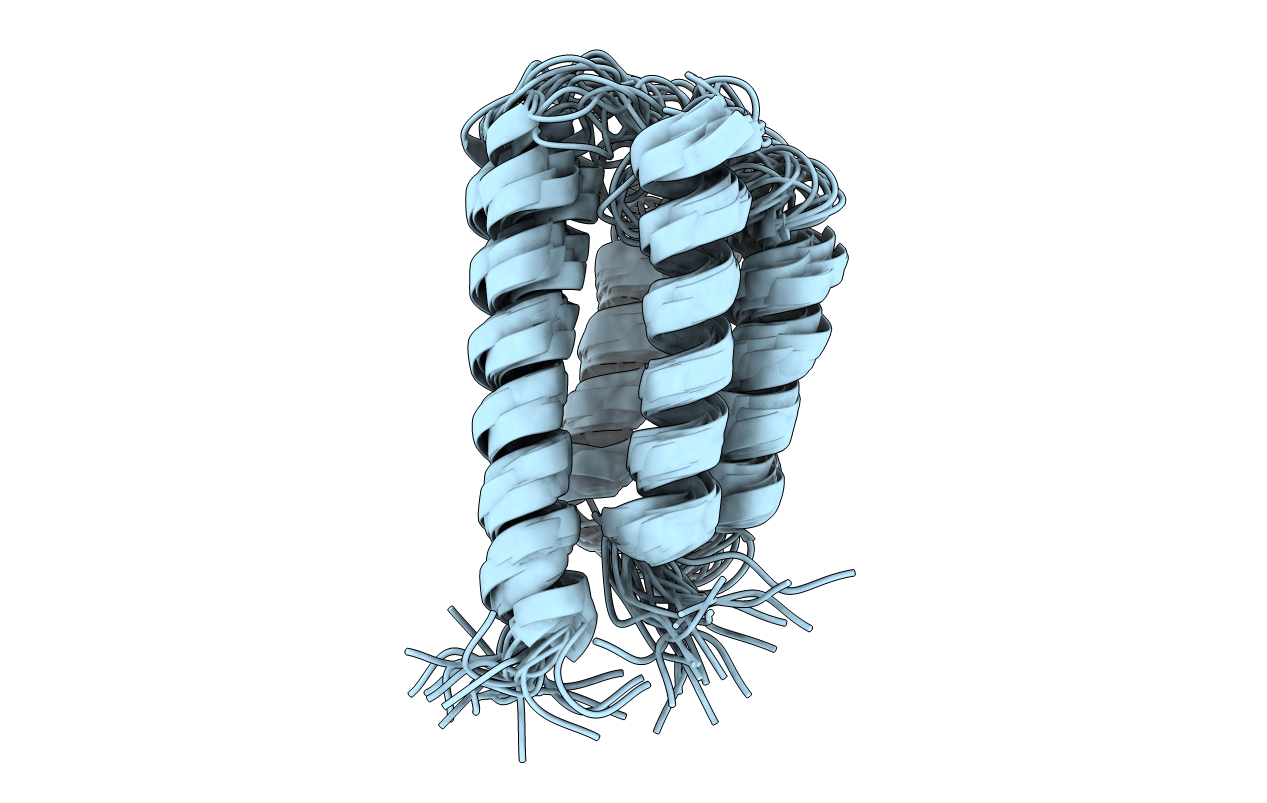
Deposition Date
2010-01-03
Release Date
2010-03-02
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2KSF
Keywords:
Title:
Backbone structure of the membrane domain of E. coli histidine kinase receptor KdpD, Center for Structures of Membrane Proteins (CSMP) target 4312C
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 83333)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy