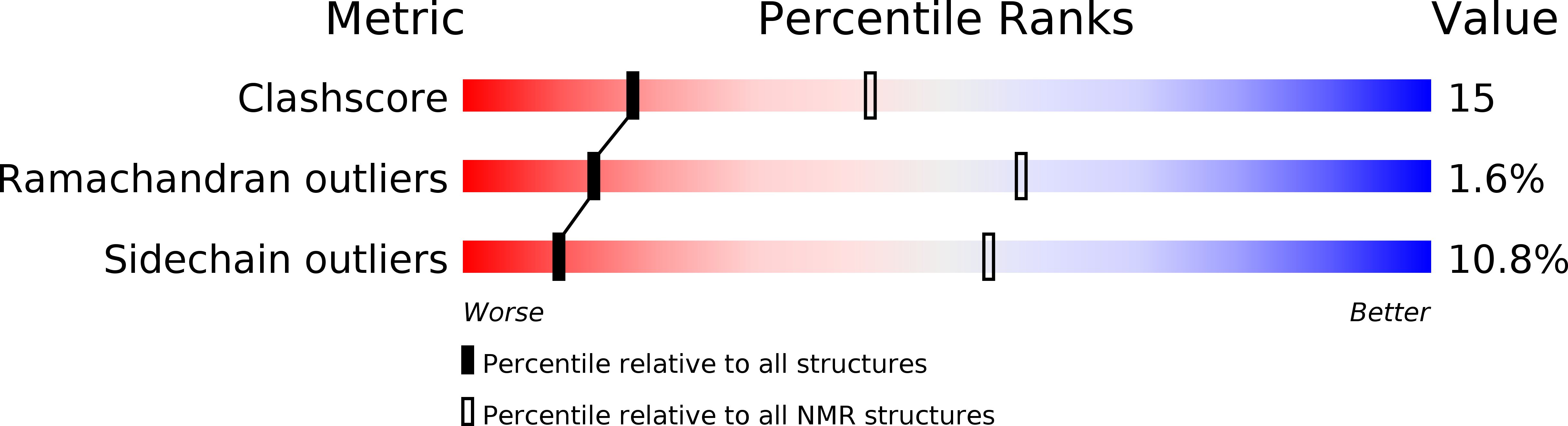Deposition Date
2009-07-28
Release Date
2009-12-29
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2KMG
Keywords:
Title:
The structure of the KlcA and ArdB proteins show a novel fold and antirestriction activity against Type I DNA restriction systems in vivo but not in vitro
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bordetella pertussis (Taxon ID: 520)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy