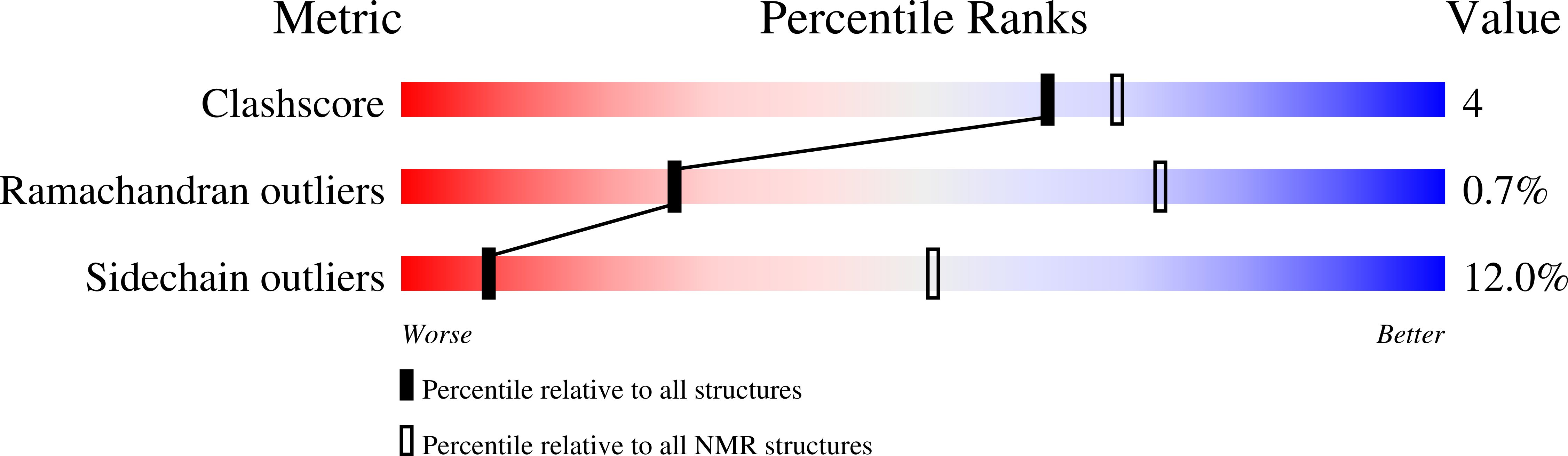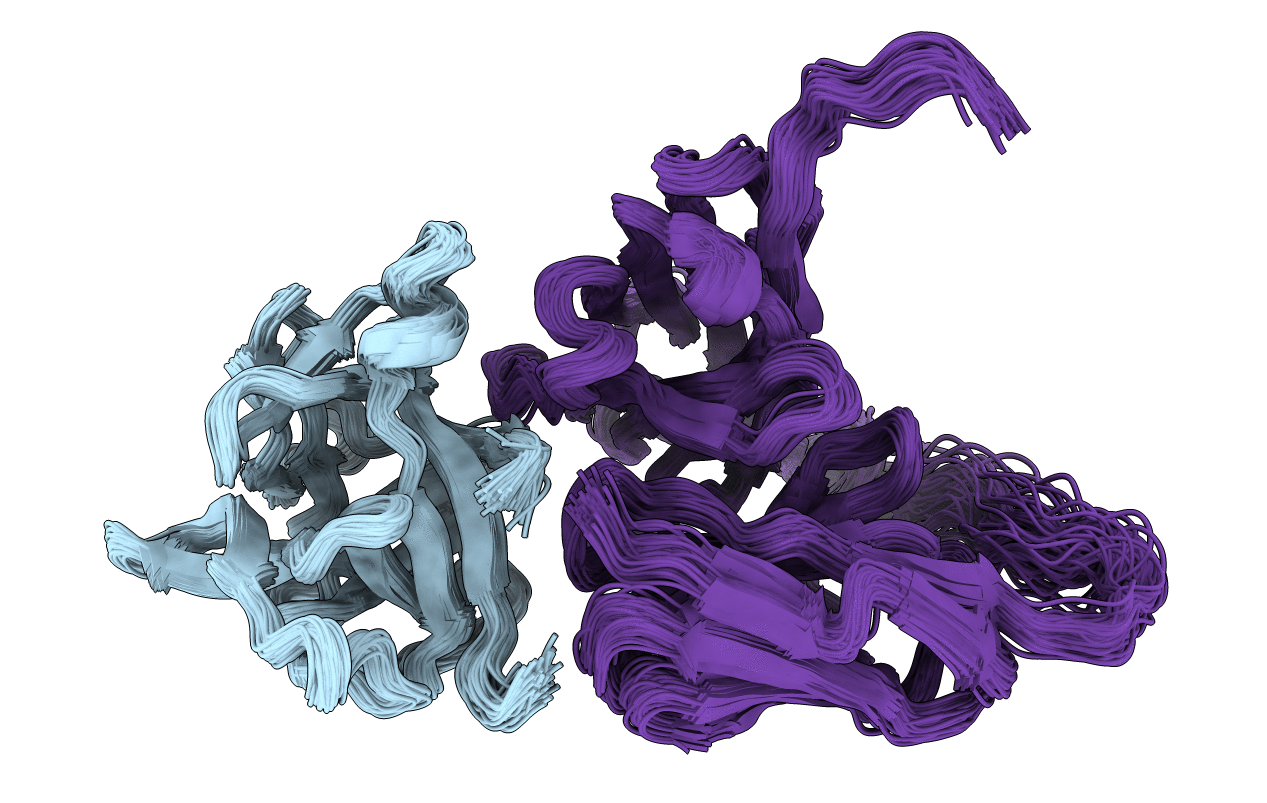
Deposition Date
2009-03-23
Release Date
2009-09-08
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
77
Conformers Submitted:
77
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted