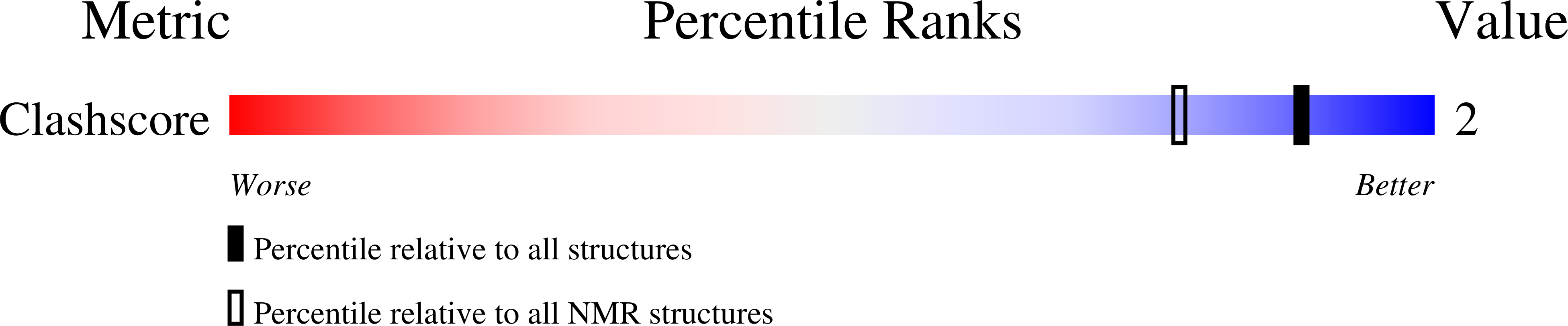
Deposition Date
2009-01-05
Release Date
2009-04-21
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2KD9
Keywords:
Title:
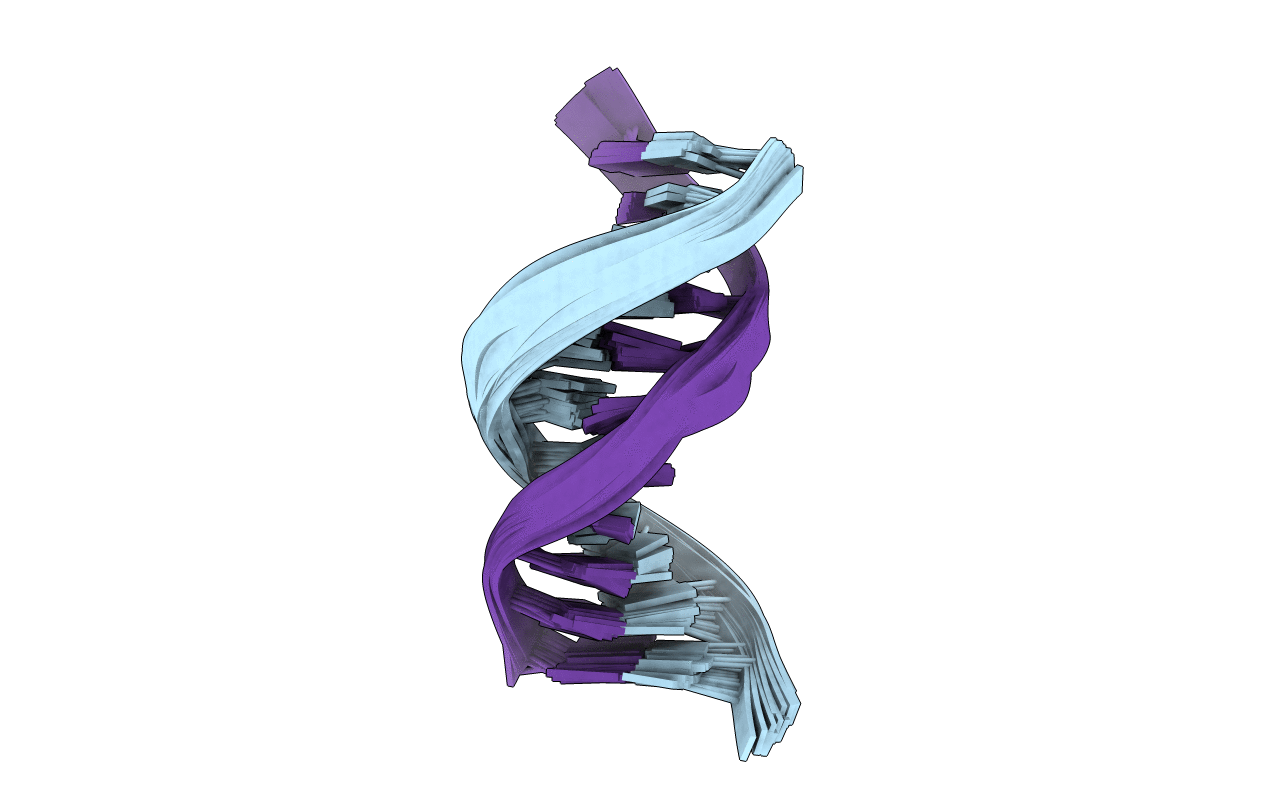
Solution Structure of DNA Containing Alpha-OH-PdG: the Mutagenic Adduct Produced by Acrolein
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
25
Conformers Submitted:
26
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted