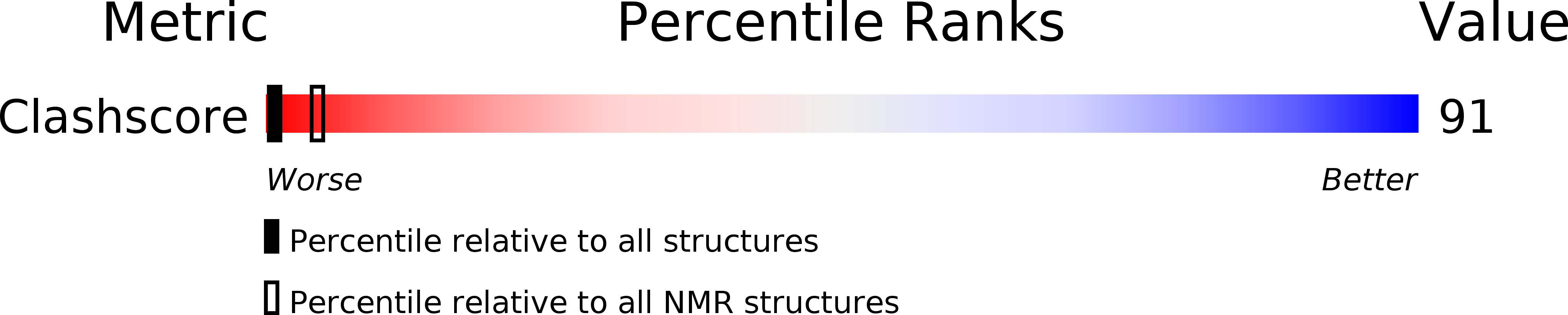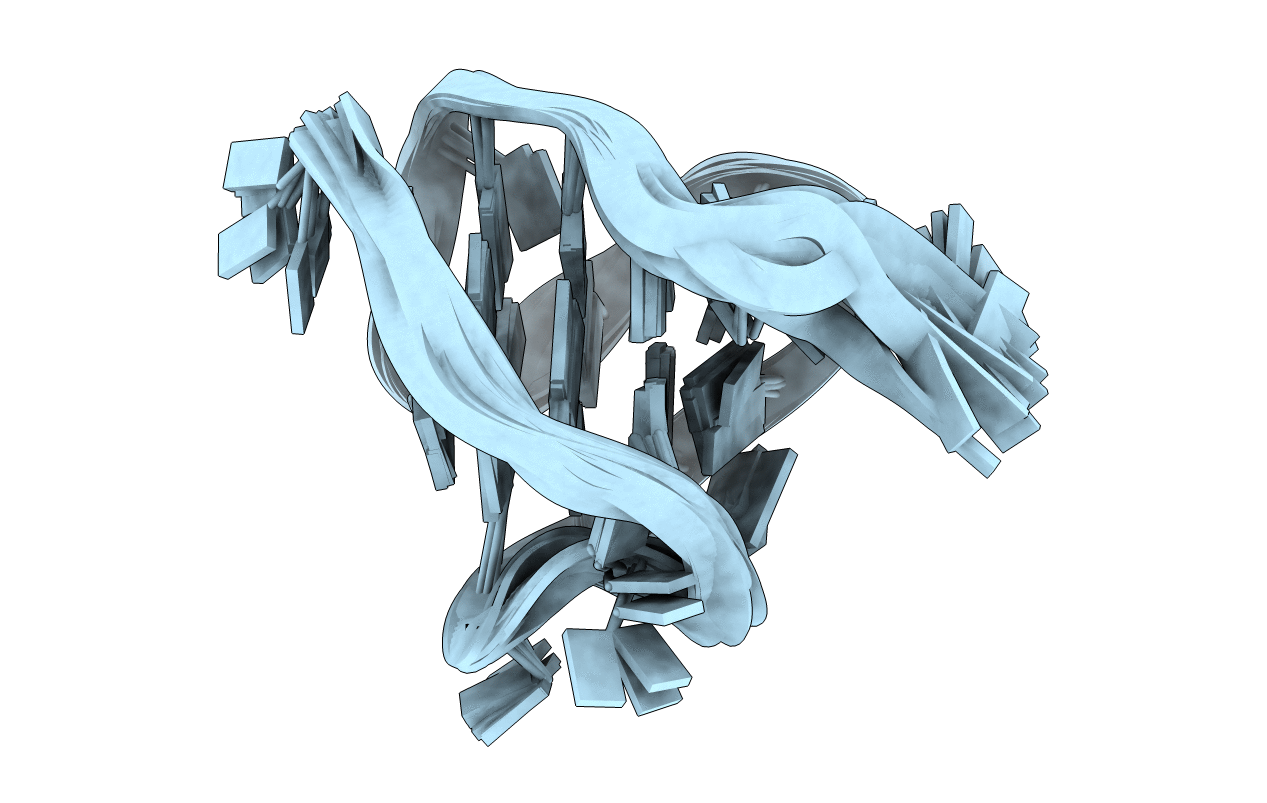
Deposition Date
2007-05-25
Release Date
2007-12-04
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2JPZ
Keywords:
Title:
Human telomere DNA quadruplex structure in K+ solution hybrid-2 form
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy