Deposition Date
2007-01-11
Release Date
2007-02-27
Last Version Date
2023-12-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2JDQ
Keywords:
Title:
C-terminal domain of influenza A virus polymerase PB2 subunit in complex with human importin alpha5
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HOMO SAPIENS (Taxon ID: 9606)
INFLUENZA A VIRUS (Taxon ID: 11320)
INFLUENZA A VIRUS (Taxon ID: 11320)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
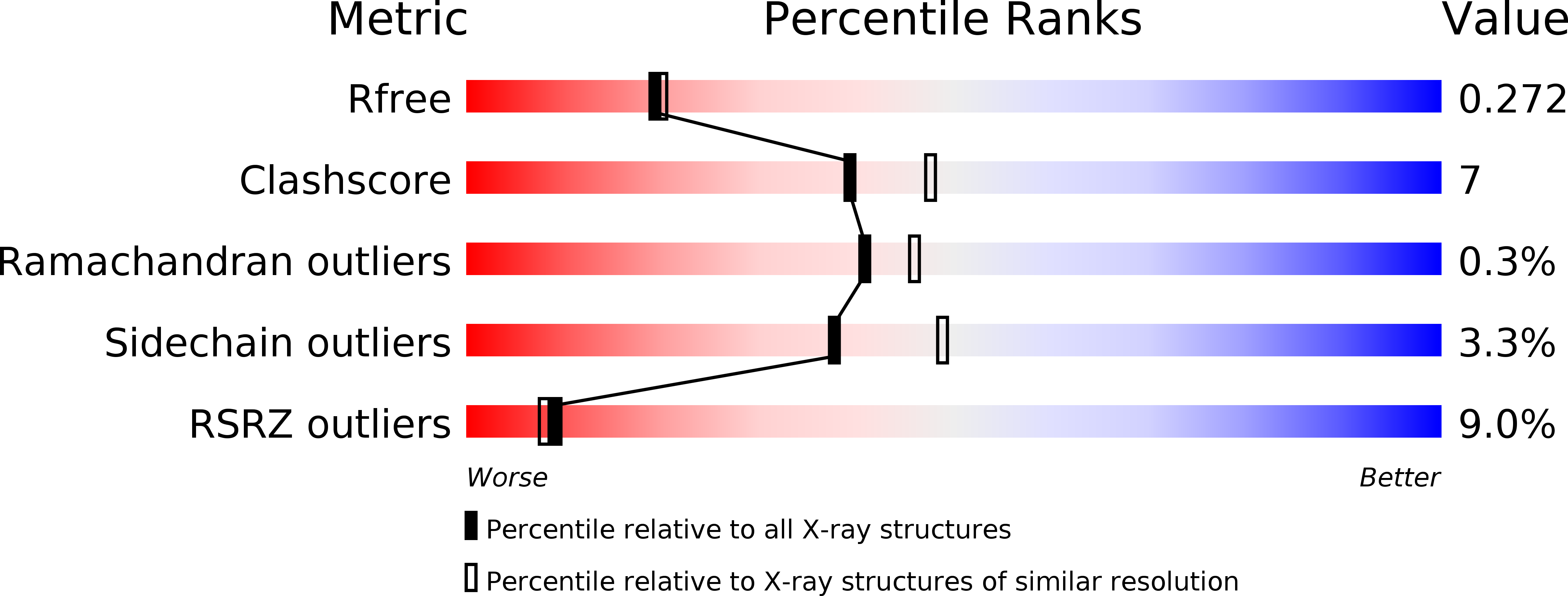
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 21 21 21