Deposition Date
2006-08-31
Release Date
2007-08-14
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
2I7O
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of Re(4,7-dimethyl-phen)(Thr124His)(Lys122Trp)(His83Gln)AzCu(II), a Rhenium modified Azurin mutant
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
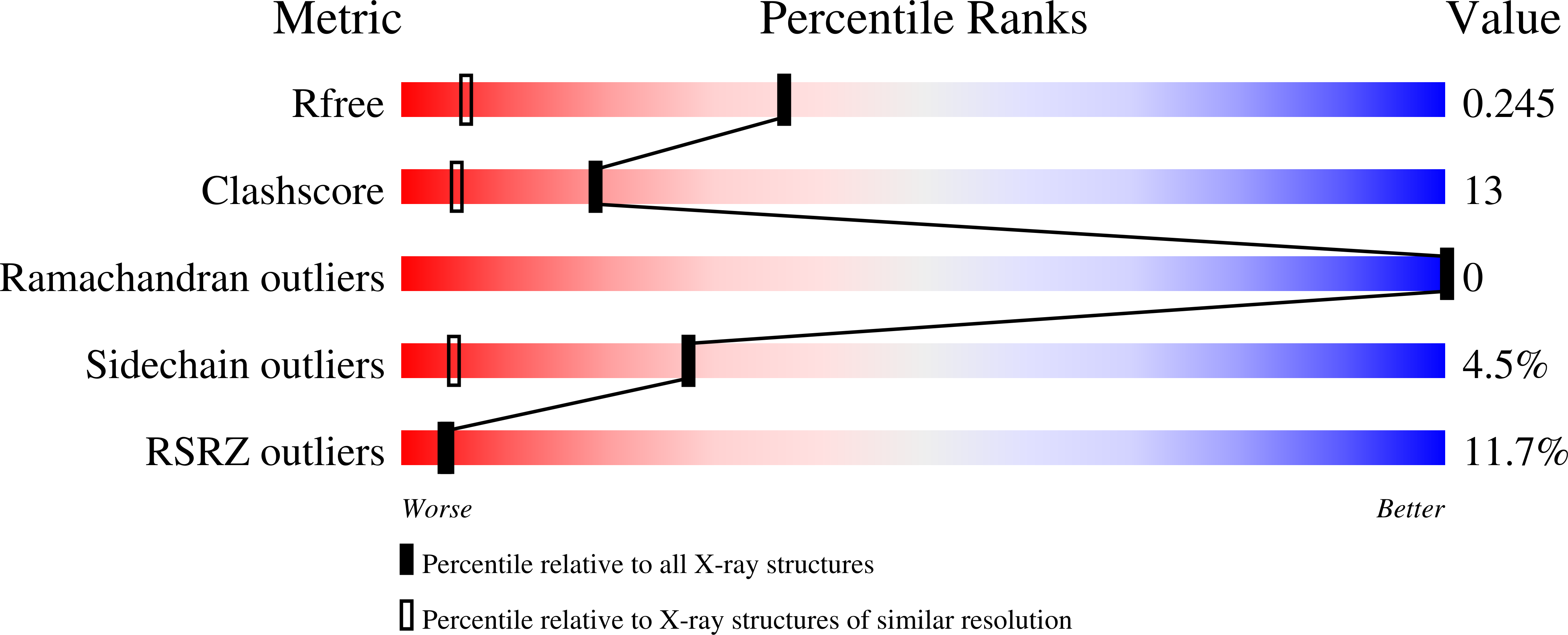
Resolution:
1.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.23
Space Group:
I 2 2 2